Themed collection Multivalent Biomolecular Recognition

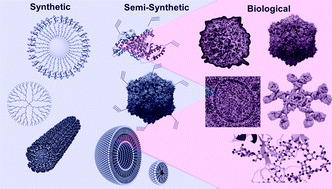
Synthetic multivalency for biological applications
Current directions and emerging possibilities under investigation for the integration of synthetic and semi-synthetic multivalent architectures with biology are discussed. Attention is focussed around multivalent interactions, their fundamental role in biology, and approaches in emulating them in terms of structure and functionality using synthetic architectures.
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 10590-10599
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01357G
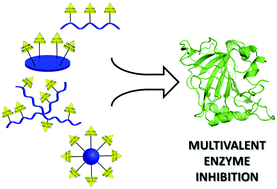
Emerging trends in enzyme inhibition by multivalent nanoconstructs
This review highlights the recent implementation of multivalent nanoconstructs in enzyme inhibition and discusses the emerging trends in their design and identification.
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 9894-9906
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01405K
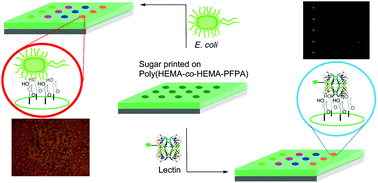
Fabrication of carbohydrate microarrays on a poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-based photoactive substrate
A carbohydrate microarray was fabricated on a PHEMA-based photoactive polymer. The arrays showed strong signals, and were used to probe carbohydrate-mediated interactions with lectin and bacteria.
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016,14, 1124-1130
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01417D
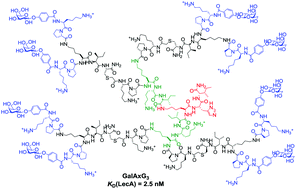
Multivalency effects on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm inhibition and dispersal by glycopeptide dendrimers targeting lectin LecA
The octagalactosylated G3 peptide dendrimer GalAxG3 was obtained by convergent synthesis, bound tightly to lectin LecA, and showed strong Pseudomonas aerguinosa biofilm inhibition and dispersal activity.
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016,14, 138-148
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01682G
Divergent and convergent synthesis of GalNAc-conjugated dendrimers using dual orthogonal ligations
We report a synthetic strategy to prepare hexadecavalent glycodendrimers that can be used in both divergent and convergent route with similar efficiency.
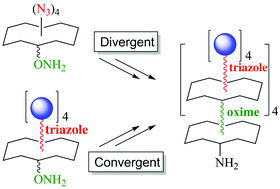
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 11529-11538
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01870F
Inhibition profiles of mono- and polyvalent FimH antagonists against 10 different Escherichia coli strains
E. coli antiadhesives were synthesized and assessed against E. coli strains isolated from patients with cystitis, osteoarticular infections or Crohn's disease.
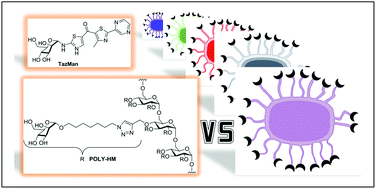
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 11369-11375
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01581B
Importance of topology for glycocluster binding to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia ambifaria bacterial lectins
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia ambifaria are two opportunistic bacteria and major infectious agents involved in infection of cystic fibrosis patients.
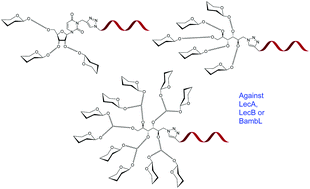
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 11244-11254
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01445J
Thiourea-based spacers in potent divalent inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence lectin LecA
A thiourea spacer adopts an extended conformation and forms the basis of a potent bivalent ligand for Pseudomonas aeruginosa lectin LecA.
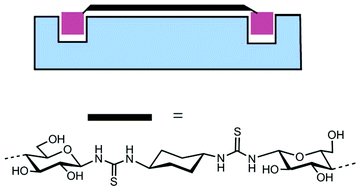
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 10923-10928
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01452B
A versatile approach towards multivalent saccharide displays on magnetic nanoparticles and phospholipid vesicles
A simple synthetic route to lipid, resorcinol and catechol adducts of saccharides has been developed, and used to give multivalent displays on the surface of nanostructures for cell targeting.
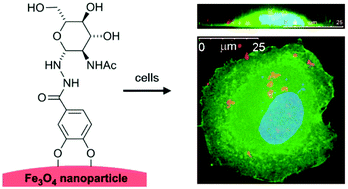
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 10751-10761
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01591J
Enhanced immunogenicity of multivalent MUC1 glycopeptide antitumour vaccines based on hyperbranched polymers
A fully synthetic multivalent MUC1 glycopeptide vaccine based on a hyperbranched polyglycerol core induced IgG antibodies which strongly recognise epithelial tumour cells.
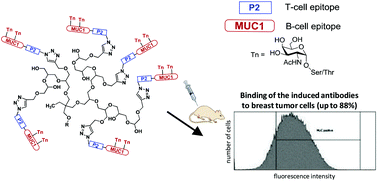
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 10150-10154
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01255D
Differential detergent sensitivity of extracellular vesicle subpopulations
This work shows for the first time that exosomes are more resistant to detergents than microvesicles and apoptotic bodies.
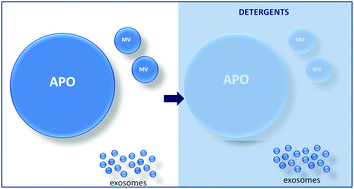
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 9775-9782
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01451D
Multivalent DNA recognition by self-assembled clusters: deciphering structural effects by fragments screening and evaluation as siRNA vectors
Fragment self-assembly was used for producing clusters with a variety of scaffolds and ligands, and an effective siRNA vector was identified.
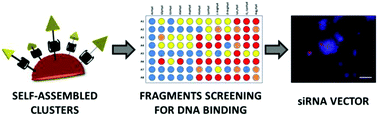
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 9427-9438
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01404B
Experimental design, modeling and optimization of polyplex formation between DNA oligonucleotides and branched polyethylenimine
The complexes formed by DNA and polycations have received great attention owing to their potential application in gene therapy.
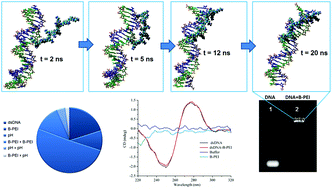
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 9445-9456
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01189B
Dynamic constitutional frameworks (DCFs) as nanovectors for cellular delivery of DNA
We introduce Dynamic Constitutional Frameworks (DCFs), macromolecular structures that efficiently bind and transfect double stranded DNA.
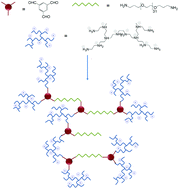
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 9005-9011
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01315A
Mannose-centered aromatic galactoclusters inhibit the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Two galactosylated glycoclusters show high affinity for LecA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and anti-biofilm activity.
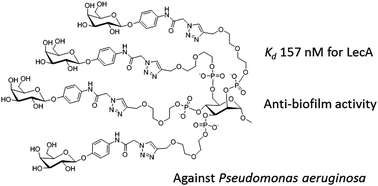
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 8433-8444
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB00948K
O-GlcNAcylation of the human epidermal growth factor receptor
The cartoon represents the EGFR at the plasma membrane where serine/threonine residues could be subjected to phosphorylation/dephosphorylation events by protein kinases (PK) and phospho-protein phosphatases (PPP) and to O-GlcNAcylation/deGlcNAcylation events by O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT) and O-linked β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (OGA).

Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 8196-8204
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB00443H
Exploring carbonic anhydrase inhibition with multimeric coumarins displayed on a fullerene scaffold
This study reports the first synthesis of multimeric suicide inhibitors of carbonic anhydrases.
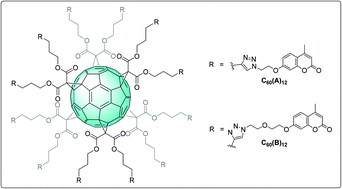
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 7445-7451
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01005E
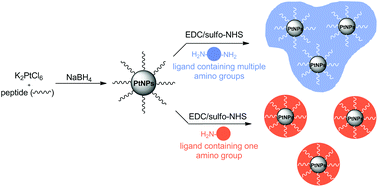
Cell-targeted platinum nanoparticles and nanoparticle clusters
The facile preparation of cell-targeted platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) is described, using designed peptides that as a single molecule control PtNP cluster growth, stabilise clusters in aqueous suspension and enable attachment of a versatile range of cell-targeting ligands.
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 6567-6572
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB00822K
Fucofullerenes as tight ligands of RSL and LecB, two bacterial lectins
A series of water-soluble glycofullerenes containing up to 24 fucose residues were tested against the two bacterial lectins LecB and RSL, and C60(E)12 bearing 24 fucose residues appeared to be the best known inhibitor of both lectins to date.

Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 6482-6492
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB00689A
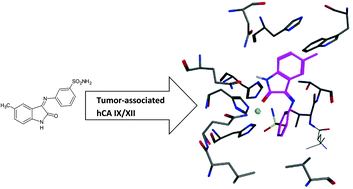
Discovery of novel isatin-based sulfonamides with potent and selective inhibition of the tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isoforms IX and XII
A series of 2/3/4-[(2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene)amino]benzenesulfonamides, obtained from substituted isatins and 2-, 3- or 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide, showed low nanomolar inhibitory activity against the tumor associated carbonic anhydrases IX and XII.
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 6493-6499
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB00688K
Heparan sulfate phage display antibodies recognise epitopes defined by a combination of sugar sequence and cation binding
Sugar sequence and M+ binding defines HS phage display Ab recognition.

Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 6066-6072
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB00564G
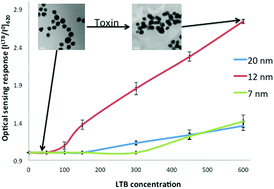
Size-optimized galactose-capped gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric detection of heat-labile enterotoxin at nanomolar concentrations
Galactose-capped gold nanoparticles size-dependently sense the bacterial lectin, heat-labile enterotoxin, allowing selective colorimetric toxin detection at 100 nM.
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015,13, 5215-5223
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB00447K
About this collection
The understanding and control of multivalent biomolecular interactions has become one of the key frontiers of chemistry and biology. This themed collection highlights some of the important findings and advances in the field, in order to:
- Develop functional sugar decorated nanoplatforms (nanoparticles, nanostructured surfaces, vesicles, microarrays, etc.).
- Understand the biomolecular mechanisms by exploring their synergistic adaptive interactions with biomolecules, in order to accurately control the chemical/biological responses.
The collection is Guest Edited by Professors Mihail Barboiu (Institut Européen des Membranes, France), Olof Ramström (KTH - Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden) and Stéphane Vincent (University of Namur, Belgium). New articles will be added to this collection as they are published.