Themed collection Iron in Biology

Iron in biology
Welcome to this Metallomics themed collection on iron in biology, guest edited by Vincenzo Abbate and Robert Hider.

Metallomics, 2017,9, 1467-1469
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT90039B
The workings of ferritin: a crossroad of opinions
Widely divergent views emerge on the central steps in the uptake, catalytic oxidation, and transfer of iron ions by ferritin.
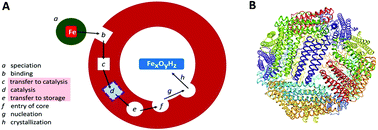
Metallomics, 2017,9, 595-605
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00124J
Intracellular iron and heme trafficking and metabolism in developing erythroblasts
Vertebrate red blood cells (RBCs) arise from erythroblasts in the human bone marrow through a process known as erythropoiesis.
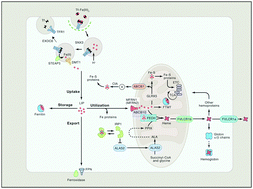
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1193-1203
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00103G
Iron homeostasis in plants – a brief overview
Iron plays a crucial role in biochemistry and is an essential micronutrient for plants and humans alike. Recent progress in the field has led to a better understanding of iron homeostasis in plants, and aided the production of high iron crops for improved human nutrition.
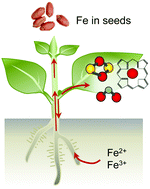
Metallomics, 2017,9, 813-823
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00136C
Hepcidin: a real-time biomarker of iron need
There are numerous blood-based biomarkers for assessing iron stores, but all come with certain limitations.
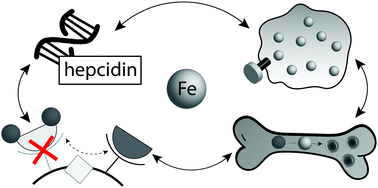
Metallomics, 2017,9, 606-618
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00047B
Linking iron-deficiency with allergy: role of molecular allergens and the microbiome
Atopic individuals are often iron-deficient and tend to develop a Th2 dominant immune response, resulting in hyperresponsiveness to harmless antigens, termed allergens.
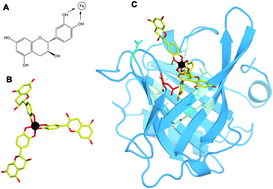
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1676-1692
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00241F
The elemental role of iron in DNA synthesis and repair
Iron is an essential redox element that functions as a cofactor in many metabolic pathways.
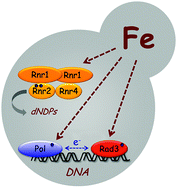
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1483-1500
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00116A
The transferrin receptor: the cellular iron gate
The transferrin receptor (TfR1), which mediates cellular iron uptake through clathrin-dependent endocytosis of iron-loaded transferrin, plays a key role in iron homeostasis.
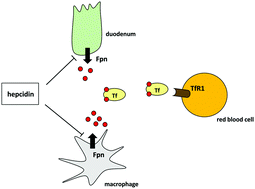
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1367-1375
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00143F
Heme-containing enzymes and inhibitors for tryptophan metabolism
Iron-containing enzymes such as heme enzymes play crucial roles in biological systems.
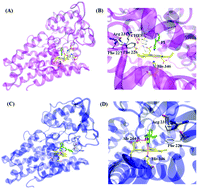
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1230-1240
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00105C
Influence of iron metabolism on manganese transport and toxicity
The structural and chemical similarities between manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe) allow the two metals to interact with each other in biological systems.
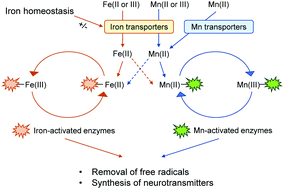
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1028-1046
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00079K
Biosynthetic considerations of triscatechol siderophores framed on serine and threonine macrolactone scaffolds
The biosyntheses of a family of enterobactin variants – amino acid substitution, insertion, and derivatization, and macrolactone expansion – is reviewed.
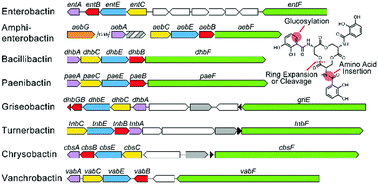
Metallomics, 2017,9, 824-839
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00111H
Ferrous iron efflux systems in bacteria
Iron efflux transporters play a critical role in protecting cells from iron intoxication.
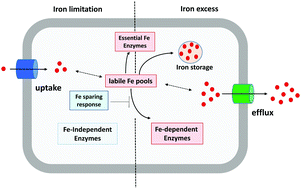
Metallomics, 2017,9, 840-851
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00112F
Mechanistic insight into the heme-independent interplay between iron and carbon monoxide in CFTR and Slo1 BKCa channels
Two pairs of Fe(II) (orange) tightly bound to two putative Fe(II) bowls (forest green) may bridge neighboring protein residues (red) in each gating ring of Slo1 BKCa for channel closure. The binding of Ca(II) (green) to the gating ring or the binding of carbon monoxide to either binuclear Fe(II) bowl may disrupt the Fe(II) bridge for channel opening but retain Fe(II) in the bowl.
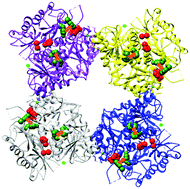
Metallomics, 2017,9, 634-645
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00065K
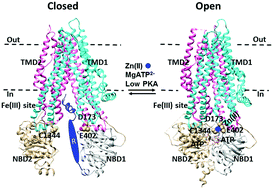
Removal of the Fe(III) site promotes activation of the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator by high-affinity Zn(II) binding
High-affinity Zn(II) bridging C1344 of nucleotide-binding domain 2 (NBD2) with E402 of NBD1, D173 of intracellular loop1 (ICL1) and the adenine group of ATP at the degenerate site may stimulate channel opening of poorly-phosphorylated human CFTR once the high-affinity Fe(III) site at the interface of the regulatory (R) domain and ICL3 is removed.
Metallomics, 2018,10, 240-247
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00315C
Duodenal cytochrome b (Cybrd1) ferric reductase functional studies in cells
A single nucleotide polymorphism (rs10455) in the last exon of the Dcytb gene in C282Y hemochromatosis subjects exhibited increased ferric reductase activity in transgenic CHO cells.

Metallomics, 2017,9, 1389-1393
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00254H
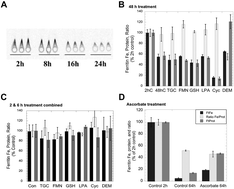
Mobilization of iron from ferritin: new steps and details
Much evidence indicates that iron stored in ferritin is mobilized through protein degradation in lysosomes, but concerns about this process have lingered, and mechanistic details of its aspects are lacking.
Metallomics, 2018,10, 154-168
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00284J
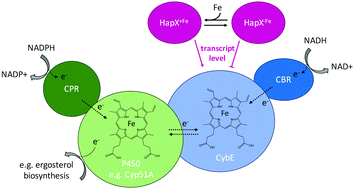
The cytochrome b5 CybE is regulated by iron availability and is crucial for azole resistance in A. fumigatus
Cytochrome P450 enzymes (P450) play essential roles in redox metabolism in all domains of life including detoxification reactions and sterol biosynthesis.
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1655-1665
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00110J
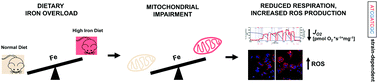
Dietary iron loading negatively affects liver mitochondrial function
Dietary iron overload affects liver metabolic homeostasis, reducing mitochondrial respiratory capacity, and increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, in a strain-dependent manner.
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1634-1644
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00177K
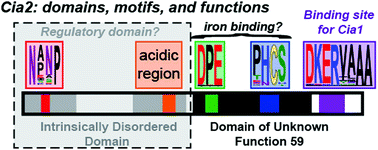
Defining the domains of Cia2 required for its essential function in vivo and in vitro
Systematic mutation of Cia2's conserved motifs reveals the Cia1 binding site and suggests Cia2 has an additional, currently cryptic, function.
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1645-1654
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00181A
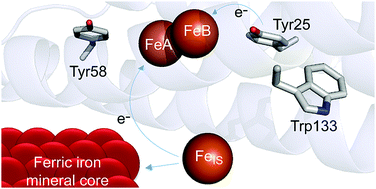
Tyr25, Tyr58 and Trp133 of Escherichia coli bacterioferritin transfer electrons between iron in the central cavity and the ferroxidase centre
Tyr58 and Trp133 play key roles in the formation and decay of the Tyr25 radical species of E. coli BFR.
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1421-1428
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00187H
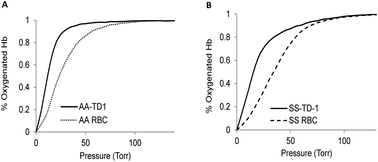
Targeting βCys93 in hemoglobin S with an antisickling agent possessing dual allosteric and antioxidant effects
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an inherited blood disorder caused by a β globin gene mutation of hemoglobin (HbS). TD-1 enhances oxygen affinity and prevents sickling of SS RBCs as well as providing protection against iron oxidation.
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1260-1270
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00104E
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Grx4 regulates the transcriptional repressor Php4 via [2Fe–2S] cluster binding
Grx4 forms a cysteine-ligated [2Fe–2S] binding complex with the transcriptional repressor Php4 to regulate transcription of iron utilization genes.
![Graphical abstract: Schizosaccharomyces pombe Grx4 regulates the transcriptional repressor Php4 via [2Fe–2S] cluster binding](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C7MT00144D&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2017)
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1096-1105
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00144D
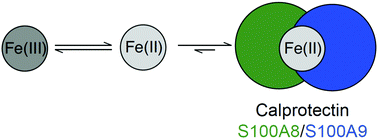
Human calprotectin affects the redox speciation of iron
The metal-chelating host-defense protein human calprotectin promotes the reduction of Fe(III) to Fe(II).
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1086-1095
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00044H
Mechanisms of iron and copper–frataxin interactions
Investigation of the mechanisms of mitochondrial metal binding to frataxin in vitro.
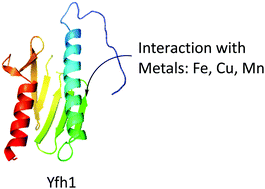
Metallomics, 2017,9, 1073-1085
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00031F
BRUTUS and its paralogs, BTS LIKE1 and BTS LIKE2, encode important negative regulators of the iron deficiency response in Arabidopsis thaliana
BTS family members negatively regulate the Fe deficiency response; mutants have increased Fe levels and tolerance to Fe deficiency.
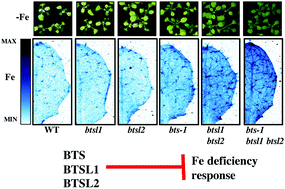
Metallomics, 2017,9, 876-890
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00152E
Analogues of desferrioxamine B designed to attenuate iron-mediated neurodegeneration: synthesis, characterisation and activity in the MPTP-mouse model of Parkinson's disease
One dual-function (2) and one first-generation (9) conjugate of the Fe(III) chelator desferrioxamine B (DFOB, 1) showed significant rescue of neurons in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease.
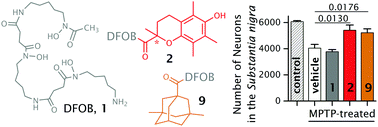
Metallomics, 2017,9, 852-864
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00039A
Zinc and the iron donor frataxin regulate oligomerization of the scaffold protein to form new Fe–S cluster assembly centers
During Fe–S cluster synthesis, oligomerization of the scaffold enables stable contacts with the iron- and sulfur-donor, with structural features predicted to facilitate cluster assembly and delivery.
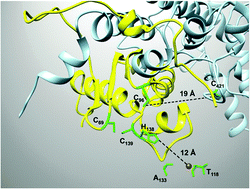
Metallomics, 2017,9, 773-801
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00089H
Flexible aspartates propel iron to the ferroxidation sites along pathways stabilized by a conserved arginine in Dps proteins from Mycobacterium smegmatis
Flexible aspartates propel iron to the ferroxidation centre (FOC) in miniferritins.
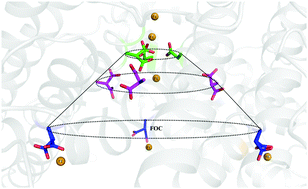
Metallomics, 2017,9, 685-698
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00008A
Inhibiting the BfrB:Bfd interaction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes irreversible iron accumulation in bacterioferritin and iron deficiency in the bacterial cytosol
The BfrB:Bfd interaction enables a dynamic equilibrium between free cytosolic Fe2+ and Fe3+ in BfrB, which functions as a buffer to oppose large fluctuations of free cytosolic Fe2+.
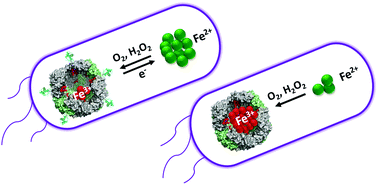
Metallomics, 2017,9, 646-659
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00042A
About this collection
This collection will highlight the latest high-impact research in iron in biology and its role in agriculture, health and disease. Covering topics such as iron uptake in microorganisms, plants and parasites, iron deficiency or overload, and iron chelation therapy as well as the role of haem and haemoproteins, iron homeostasis, iron transport and storage proteins, and Fe-S clusters. Guest Edited by Vincenzo Abbate and Robert Hider. New articles will be added to this collection as they are published.
Also of interest
Binding, Transport and Storage of Metal Ions in Biological Cells
Editors: Wolfgang Maret and Anthony Wedd
This book is structured around the periodic table and focuses on the control of metal ions in cells. It addresses the molecular aspects of binding, transport and storage that ensure balanced levels of the essential elements. This book is the first to comprehensively survey the molecular nature of the overall natural balance of metal ions in nutrition, toxicology and pharmacology. It is written as an introduction to research for students and researchers in academia and industry and begins with a chapter by Professor R J P Williams FRS.