Themed collection Drinking Water Exposome

Front cover

The drinking water exposome
Guest editors Peter Vikesland and Lutgarde Raskin introduce the Drinking Water Exposome themed issue of Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology.

Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 561-564
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW90016J
Emerging investigators series: the efficacy of chlorine photolysis as an advanced oxidation process for drinking water treatment
The photolysis of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and hypochlorite (OCl−) produces a suite of reactive oxidants, including hydroxyl radicals (˙OH), chlorine radicals (Cl˙), and ozone (O3).
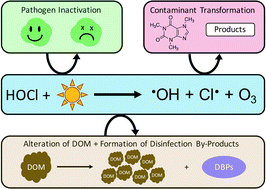
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 565-579
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00029K
A human exposome framework for guiding risk management and holistic assessment of recycled water quality
In this critical review, we propose that the “human exposome” concept provides guiding principles for water reuse risk management strategies.
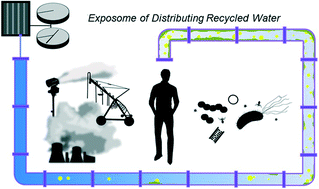
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 580-598
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00031B
Characterising and understanding the impact of microbial biofilms and the extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) matrix in drinking water distribution systems
Drinking water distribution systems (DWDS) contain complex microbial biofilm communities. Understanding the ecology of these biofilms is critical for effective management of DWDS infrastructure and maintenance of water quality.
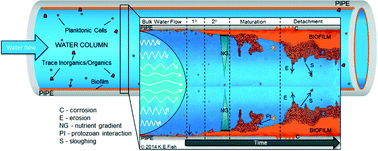
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 614-630
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00039H
Critical review of mathematical approaches for quantitative microbial risk assessment (QMRA) of Legionella in engineered water systems: research gaps and a new framework
Legionella has been identified as the responsible agent for two-thirds of waterborne disease outbreaks in the United States from 2011–2012.
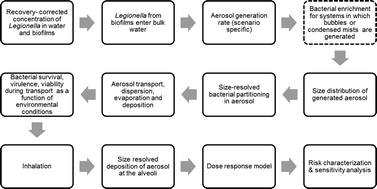
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 599-613
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00023A
Eukaryotic community diversity and spatial variation during drinking water production (by seawater desalination) and distribution in a full-scale network
Characterization of eukaryotic community dominated by fungi for drinking water distribution network fed by reverse osmosis seawater desalination plant.
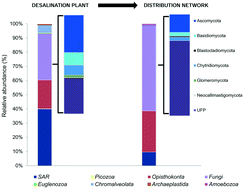
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2017,3, 92-105
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00265J
Resilience of microbial communities in a simulated drinking water distribution system subjected to disturbances: role of conditionally rare taxa and potential implications for antibiotic-resistant bacteria
CIRCOS plots representing the pan-genome and resistome of waterborne resistant bacteria.
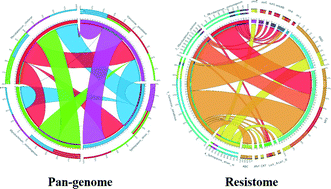
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 645-657
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00053C
A new dipstick colorimetric sensor for detection of arsenate in drinking water
The first ever dipstick sensing of arsenate through visual observation without any instrumentation.
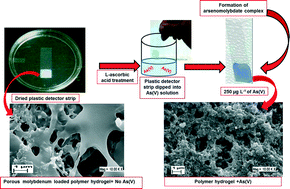
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 693-704
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EW00276A
Emerging investigators series: microbial communities in full-scale drinking water distribution systems – a meta-analysis
In this study, we co-analyze all available 16S rRNA gene sequencing studies from bulk drinking water samples in full-scale drinking water distribution systems.
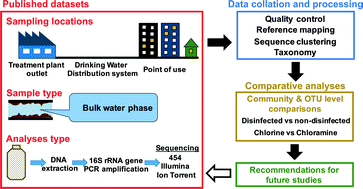
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 631-644
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00030D
A survey of indicator parameters to monitor regrowth in unchlorinated drinking water
The objective of our study was to explore microbiological parameters that are suitable as indicators for regrowth in distribution systems that receive unchlorinated drinking water in the Netherlands.
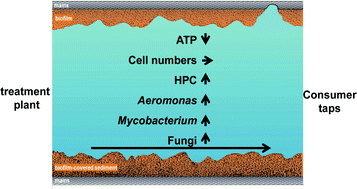
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 683-692
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00007J
Biofilms in shower hoses – choice of pipe material influences bacterial growth and communities
Flexible polymeric pipe materials are commonly used as shower hoses or connections to faucets in the last meters of building plumbing, but these tend to leach high concentrations of carbon that encourage bacterial growth.
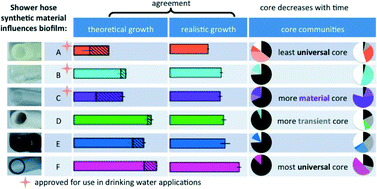
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 670-682
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00016A
Archaeal ammonium oxidation coupled with bacterial nitrite oxidation in a simulated drinking water premise plumbing system
Simulated copper and PVC premise plumbing reactors modeling chloramine decay were monitored for complete nitrification of 0.71 mg NH4-N L−1 ammonium to nitrate with no nitrite detected.
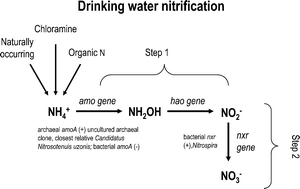
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2016,2, 658-669
https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EW00273G
About this collection
The Drinking Water Exposome has recently been defined as the environmental exposure complement to the genome. These articles utilise this construct to consider chemical and microbial exposures that can occur via consumption or use of drinking water.
Guest edited by Lutgarde Raskin (University of Michigan, USA) and Peter Vikesland (Virginia Tech, USA), this collection covers the diverse array of research topics that are encompassed by drinking water chemistry and microbiology at the interface of water quality and human health.