Themed collection Frontiers in Spectroscopic Techniques in Inorganic Chemistry

Frontiers in spectroscopic techniques in inorganic chemistry
Welcome to this issue of Dalton Transactions featuring the themed issue “Frontiers in spectroscopic techniques in inorganic chemistry”.

Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13163-13165
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT90159C
On the use of solid-state 45Sc NMR for structural investigations of molecular and silica-supported scandium amide catalysts
45Sc NMR of molecular and silica-grafted scandium amido derivatives provides information about the metal coordination sphere with links to catalytic activity.
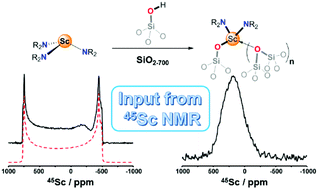
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13176-13179
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT02415K
Copper induced spin state change of heme–Aβ associated with Alzheimer's disease
Binding of Cu(II) not only drives the conversion of the benign bis-His bound low spin heme(III)–Aβ complex to the detrimental mono-His high spin form, even in the presence of excess Aβ, but it also forms the most toxic heme(III)–Cu(II)–Aβ species.
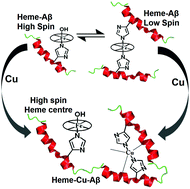
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13171-13175
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01700F
Stereochemistry of metal tetramethylcyclam complexes directed by an unexpected anion effect
An unexpected anion effect leads to the direct and selective preparation of the trans-III-[Cu(TMC)]2+ complex that is fully characterized by X-ray crystallography, UV-visible spectroscopy, advanced EPR spectroscopy, and computational studies.

Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13166-13170
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01489A
Neuroprotective alpha-cleavage of the human prion protein significantly impacts Cu(II) coordination at its His111 site
Alpha-cleavage proteolytic processing of human prion protein significantly impacts its Cu(II) coordination properties at the His111 site.
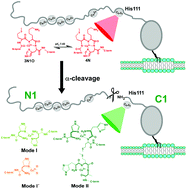
Dalton Trans., 2018,47, 9274-9282
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT03400H
Two-photon spectroscopy of tungsten(0) arylisocyanides using nanosecond-pulsed excitation
The two-photon absorption (TPA) cross sections (δ) for tungsten(0) arylisocyanides (W(CNAr)6) were determined in the 800–1000 nm region using two-photon luminescence (TPL) spectroscopy.
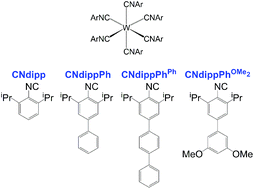
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13188-13193
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT02632C
Microsecond 3MLCT excited state lifetimes in bis-tridentate Ru(II)-complexes: significant reductions of non-radiative rate constants
A close to octahedral structure and an unusually small singlet–triplet mixing result in microsecond 3MLCT excited state lifetimes for this class of tridentate Ru(II)-complexes.
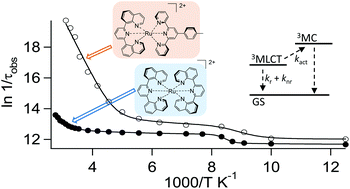
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13314-13321
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT02437A
Magnetic circular dichroism and density functional theory studies of electronic structure and bonding in cobalt(II)–N-heterocyclic carbene complexes
The combination of simple cobalt salts and N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands has been highly effective in C–H functionalization, hydroarylation and cross-coupling catalysis, though displaying a strong dependence on the identity of the NHC ligand.
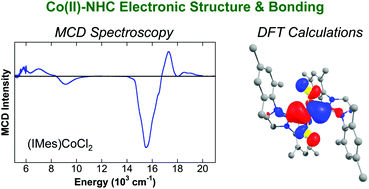
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13290-13299
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01748K
Syntheses of metallo-pseudorotaxanes, rotaxane and post-synthetically functionalized rotaxane: a comprehensive spectroscopic study and dynamic properties
Amido-amine macrocycle-based pseudorotaxanes, rotaxane, are investigated via different spectroscopic techniques, and post-synthetic functionalized rotaxane exhibits rotamer-induced reversible dynamic behaviour.
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13300-13313
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01364G
Xanthine oxidase–product complexes probe the importance of substrate/product orientation along the reaction coordinate
Resonance Raman spectroscopy has been used to probe substrate orientation and hydrogen bonding interactions in a xanthine oxidase catalytic intermediate.

Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13242-13250
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01728F
Spectroscopic and reactivity differences in metal complexes derived from sulfur containing Triphos homologs
Spectroscopic, computational, and reactivity studies shed light on the different coordination behavior of sulfur containing Triphos derived complexes.
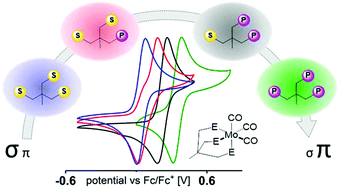
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13251-13262
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01459G
Spectroscopic and computational studies of reversible O2 binding by a cobalt complex of relevance to cysteine dioxygenase
Spectroscopic and computational studies of reversible O2 binding by a cobalt active-site mimic shed light on the catalytic mechanism of cysteine dioxygenases.
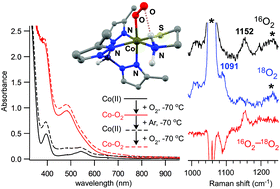
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13229-13241
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01600J
Exchangeable proton ENDOR as a probe of the redox-active iron center in activated bleomycin and ferric bleomycin
This work establishes the existence of and implies the mechanistic role of specific exchangeable protons near the Fe(III) of activated bleomycin (ABLM).
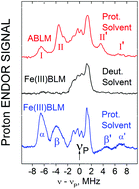
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13263-13272
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01354J
A cobalt–nitrosyl complex with a hindered hydrotris(pyrazolyl)borate coligand: detailed electronic structure, and reactivity towards dioxygen
The cobalt–nitrosyl complex [Co(NO)(L3)] is supported by a highly hindered tridentate nitrogen ligand, hydrotris(3-tertiary butyl-5-isopropyl-1-pyrazolyl)borate (denoted as L3−), and shows a linear Co–N–O unit.
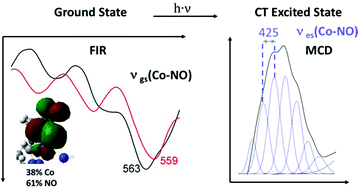
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13273-13289
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01565H
Surface enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy of iron Hangman complexes on electrodes during electrocatalytic oxygen reduction: advantages and problems of common drycast methods
The structure of drycast Hangman complexes on electrodes during electrocatalytic oxygen reduction was investigated with surface enhanced Raman spectro-electrochemistry.
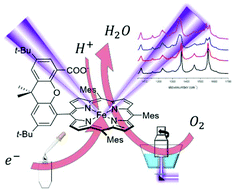
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13220-13228
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01174A
Consensus structures of the Mo(V) sites of sulfite-oxidizing enzymes derived from variable frequency pulsed EPR spectroscopy, isotopic labelling and DFT calculations
The “blocked” form of sulfite oxidase has O-bound sulfite, and only the coordinated and remote O atoms exchange with H217O.
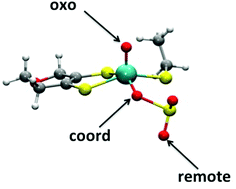
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13202-13210
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01731F
Raman spectral titration method: an informative technique for studying the complexation of uranyl with uranyl(VI)–DPA/oxalate systems as examples
Spectral titration method with Raman spectroscopy is a powerful method for studying the complexation of uranyl(VI) with various ligands.
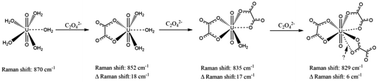
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13180-13187
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01631J
Spectroscopic evidence for cofactor–substrate interaction in the radical-SAM enzyme TYW1
EPR and Mössbauer spectroscpies provide evidence for interaction between SAM and pyruvate in the catalytic pocket of the iron-sulfur cluster enzyme TYW1.
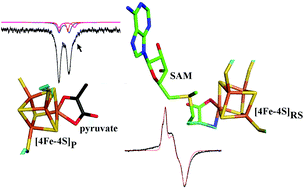
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13211-13219
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT00736A
Reaction mechanism of the metallohydrolase CpsB from Streptococcus pneumoniae, a promising target for novel antimicrobial agents
CpsB, a novel potential target for antimicrobial agents, is a dimetallic enzyme that hydrolyses phosphate ester and β-lactam bonds.
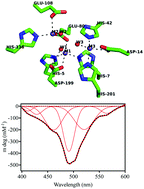
Dalton Trans., 2017,46, 13194-13201
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT01350G