Themed collection Biocatalysis

Front cover

Inside front cover

Contents list
Biocatalysis
Welcome to this themed issue of Catalysis Science & Technology entitled ‘Biocatalysis’.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1523-1523
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY90030K
Different strategies to enhance the activity of lipase catalysts
This perspective presents the recent developments on active bio-catalyst preparation by the enzyme immobilization on nanomaterials and site-specific chemical modification.
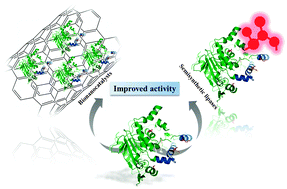
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1531-1543
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20125A
Exploiting duality in nature: industrial examples of enzymatic oxidation and reduction reactions
Enzymatic oxidation and reduction are already important reactions for the large scale production of interesting API intermediates.
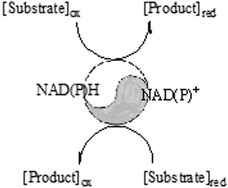
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1524-1530
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20102J
Biofilms and their engineered counterparts: A new generation of immobilised biocatalysts
The robust nature of biofilms makes them an attractive vehicle for protecting and immobilising enzymes for biotransformations. In this paper, we reflect upon recent advances in the use and generation of single species biofilms as biocatalysts to carry out industrially useful reactions.
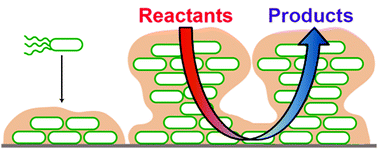
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1544-1547
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20085F
Tuning lipase activity with perfluoro carboxylic acids as additives
Choosing the right additive for tuning lipase activity: perfluorodecanoic acid (PFDA) enhanced lipase activity by 260%, whereas perfluorosebasic acid (PFSA) negatively affected it.
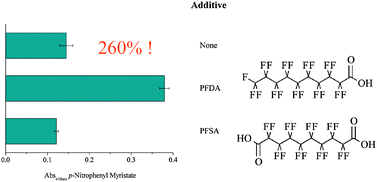
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1553-1555
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20173A
Reductive dehalogenation of β-haloacrylic ester derivatives mediated by ene-reductases
Reductive dehalogenation of β-haloacrylic esters catalysed by ene-reductases proceeded via bioreduction of the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond followed by non-enzymatic β-elimination of HX.
C bond followed by non-enzymatic β-elimination of HX.
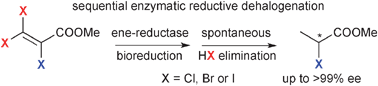
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1548-1552
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20079A
Asymmetric, biocatalytic labeled compound synthesis using transaminases
The use of transaminases for the incorporation of deuterium and tritium in chiral amines.
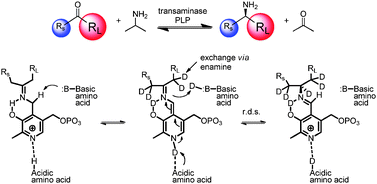
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1556-1559
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20110K
Porous cross linked enzyme aggregates (p-CLEAs) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae invertase
Porous CLEAs of invertase prepared with pore making agent starch showed improved mass transfer of sucrose compared to conventional CLEAs.
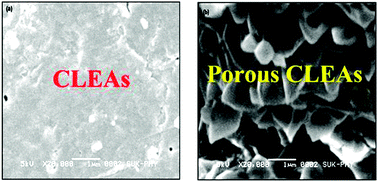
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1575-1579
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20304A
Multi-enzymatic cascade synthesis of D-fructose 6-phosphate and deoxy analogs as substrates for high-throughput aldolase screening
One-pot synthesis of sugar phosphates by artificial metabolisms, created in vitro by appropriate coupling of aldol, retro-aldol, and phosphorylation modules.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1596-1601
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20092A
Cofactor promiscuity among F420-dependent reductases enables them to catalyse both oxidation and reduction of the same substrate
Some F420-dependent reductases that use F420H2 for an enoate reduction of aflatoxin can also use FMN to oxidise aflatoxin.
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1560-1567
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20129A
Enantiopure 3-methyl-3,4-dihydroisocoumarins and 3-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines via chemoenzymatic asymmetric transformations
A new divergent and asymmetric synthetic route has been developed for the production of enantiomerically pure isocoumarin and isoquinoline derivatives.
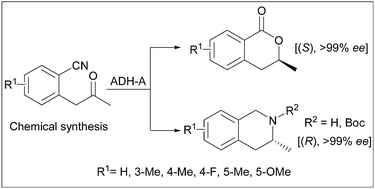
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1590-1595
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20152F
Synergy between catalysts : enzymes and bases. DKR of non-natural amino acids derivatives
A double catalyst system for the dynamic kinetic resolution of amino acid thioesters in hydrolysis, transesterification or transamidation.
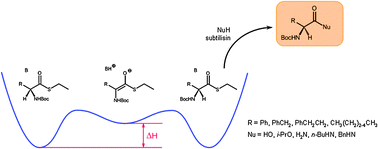
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1606-1616
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20106B
Stereoselective synthesis of bulky 1,2-diols with alcohol dehydrogenases
The potential of different alcohol dehydrogenases to reduce sterically demanding 2-hydroxy ketones towards chiral 1,2-diols with high stereoselectivity is shown.
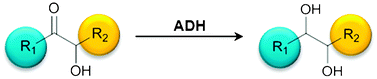
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1580-1589
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20120H
Mutational analysis of phenolic acid decarboxylase from Bacillus subtilis (BsPAD), which converts bio-derived phenolic acids to styrene derivatives
Mutational analysis, coupled with a complex structure, reveals catalytic roles for Tyr11 and Tyr13 in carboxylate recognition and for Arg41 in binding of the phenolic hydroxyl of the substrate.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1568-1574
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY20015E
Asymmetric reduction of a key intermediate of eslicarbazepine acetate using whole cell biotransformation in a biphasic medium
The reaction parameters such as pH, temperature, concentration and glucose addition were investigated for optimal output.

Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012,2, 1602-1605
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CY00537A
About this collection
This themed issue provides an overview of some of the challenges facing biocatalysis and biotechnology in meeting the demands of future chemical production.