Themed collection Surface chemistry and interface science

Surface chemistry and interface science
Surface chemistry and interface science is about phenomena at interfaces and the self-assembly of amphiphilic molecules.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23568-23569
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP90152F
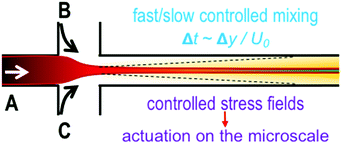
SAXS on a chip: from dynamics of phase transitions to alignment phenomena at interfaces studied with microfluidic devices
Microfluidic devices allow actuation on the microscale, while in situ SAXS allows visualization of these effects in relevant systems.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23690-23703
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02736B
Synergies in lubrication
In living organisms the aqueous medium is used for providing low friction forces. This is achieved by synergistic actions of different biomolecules that together accomplish a high load bearing capacity and sustain an easily sheared water layer.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23677-23689
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03517A
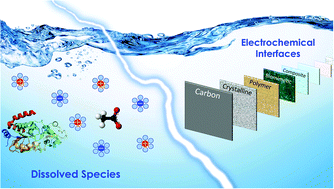
Electrosorption at functional interfaces: from molecular-level interactions to electrochemical cell design
This perspective discusses the fundamental processes behind electrosorption at charged interfaces, and highlights advances in electrode design for sustainable technologies in water purification and ion-selective separations.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23570-23584
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02822A
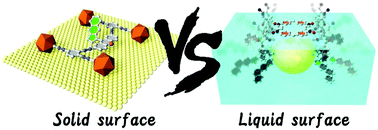
Solid surface vs. liquid surface: nanoarchitectonics, molecular machines, and DNA origami
Comparisons of science and technology between these solid and liquid surfaces would be a good navigation for current-to-future developments.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23658-23676
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02280H
The relevance of structural features of cellulose and its interactions to dissolution, regeneration, gelation and plasticization phenomena
The interactions and structural properties of cellulose influence different phenomena.
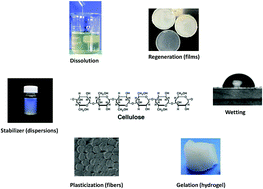
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23704-23718
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02409F
Self-thermophoretic motion of controlled assembled micro-/nanomotors
Controlled assembled micro-/nanomotors are driven in fluid by near infrared light. The behaviour and mechanism of self-thermophoretic motion are reviewed.
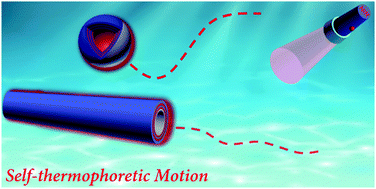
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23606-23613
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02561K
From force curves to surface nanomechanical properties
Surface science, which spans the fields of chemistry, physics, biology and materials science, requires information to be obtained on the local properties and property variations across a surface.
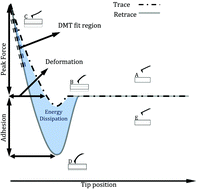
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23642-23657
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02612A
Colloidal diffusion in confined geometries
Colloidal diffusion in confined geometries is analysed at the level of anisotropic pair densities.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23632-23641
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02497E
Unifying hydrotropy under Gibbs phase rule
A rational approach, aiming at constructing a unified theory of hydrotropy, will be presented based upon the first principles of statistical thermodynamics.
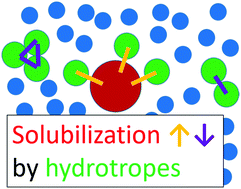
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23597-23605
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02132A
Multiscale simulations for understanding the evolution and mechanism of hierarchical peptide self-assembly
Multiscale molecular simulations that combine and systematically link several hierarchies can provide insights into the evolution and dynamics of hierarchical peptide self-assembly from the molecular level to the mesoscale.
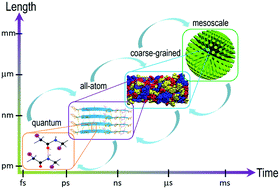
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23614-23631
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01923H
Near-infrared photochemistry at interfaces based on upconverting nanoparticles
We review near-infrared photochemistry at interfaces based on upconverting nanoparticles, highlight its potential applications, and discuss the challenges.
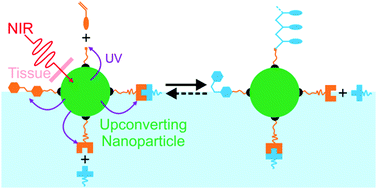
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23585-23596
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP01838J
One-step assembly of multi-layered structures with orthogonally oriented stripe-like patterns on the surface of a capillary tube
Highly-ordered, large-scale stripe patterns could be formed simultaneously on both the inner and outer surfaces of capillary tubes with orthogonal orientations.
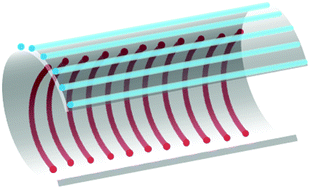
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23719-23722
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02583A
Wormlike micelles versus water-soluble polymers as rheology-modifiers: similarities and differences
Rheological behaviors and aqueous solution microstructures of wormlike micelles and a water-soluble polymer are compared.
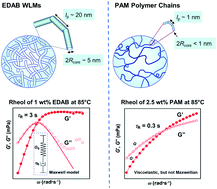
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 24458-24466
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04962E
Langmuir–Blodgett films of perylene bisimide derivatives and fluorescent recognition of diamines
A fluorescent film was constructed with the well-known Langmuir–Blodgett technique, and it showed exceptional sensing performances for some diamine vapors.
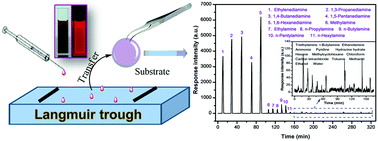
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23898-23904
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP04235C
Coating agent-induced mechanical behavior of 3D self-assembled nanocrystals
The Young's modulus of three-dimensional self-assembled Ag nanocrystals, as so-called supracrystals, is correlated with the type of coating agent as well as the nanocrystal morphology.
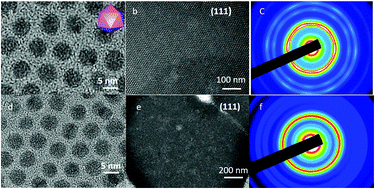
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23887-23897
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02649H
Formation of titanium dioxide core–shell microcapsules through a binary-phase spray technique
Fast and single-step formation of metal oxide core–shell particles with a loading of 50 wt% active substance.
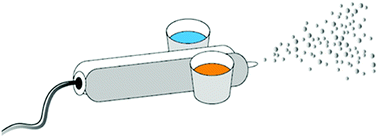
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23878-23886
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02571H
Enhanced interfacial activity of multi-arm poly(ethylene oxide) star polymers relative to linear poly(ethylene oxide) at fluid interfaces
Interfacial tension reduction, dynamic dilatational elasticity and extent of adsorption were investigated for linear poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) chains of varying molecular weight and for PEO star polymers with an average of 64 arms per star at air/water, xylene/water, and cyclohexane/water interfaces.
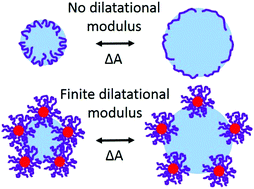
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23854-23868
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02841E
Trimethylsilyl hedgehogs – a novel class of super-efficient hydrocarbon surfactants
Presented here are the results for a novel class of hydrocarbon surfactants, termed trimethylsilyl hedgehogs (TMS-hedgehogs), due to the presence of silicon in the tails.
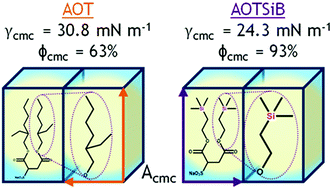
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23869-23877
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02570J
Membrane interactions and antimicrobial effects of layered double hydroxide nanoparticles
Membrane interactions are critical for the successful use of inorganic nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents and as carriers of, or co-actives with, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs).
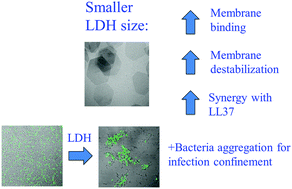
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23832-23842
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02701J
Using a chitosan nanolayer as an efficient pH buffer to protect pH-sensitive supramolecular assemblies
We propose that chitosan can be used as an efficient pH-responsive protective layer for pH sensitive soft materials.
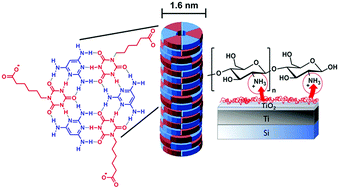
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23843-23848
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02618H
Electrostatic interactions in concentrated colloidal dispersions
An explicit expression, free from adjustable parameters, is derived for the effective pair interaction between charged colloidal spheres at high concentration in a medium containing an electrolyte.
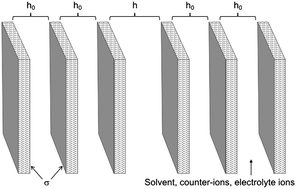
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23849-23853
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02594G
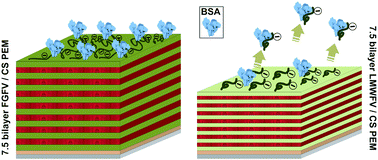
The influence of polyanion molecular weight on polyelectrolyte multilayers at surfaces: protein adsorption and protein–polysaccharide complexation/stripping on natural polysaccharide films on solid supports
Two different fucoidan polymers have been used to create substrates for protein adsorption studies.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23790-23801
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02599H
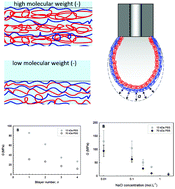
The influence of polyanion molecular weight on polyelectrolyte multilayers at surfaces: elasticity and susceptibility to saloplasticity of strongly dissociated synthetic polymers at fluid–fluid interfaces
Decreasing polyanion chain length increases the elastic modulus and saloplasticity threshold in freestanding polyelectrolyte multilayers.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23781-23789
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02614E
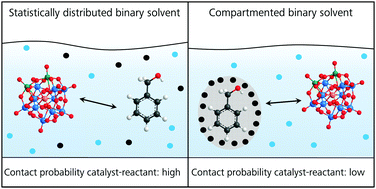
A systematic study of the influence of mesoscale structuring on the kinetics of a chemical reaction
In this contribution, we link the mesoscopic structuring of the binary structured solvent mixture H2O/tert-butanol (TBA) to the kinetics and efficacy of the oxidation of benzyl alcohol (BA) to the corresponding aldehyde catalyzed by H5PMo10V2O40.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23773-23780
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02134H
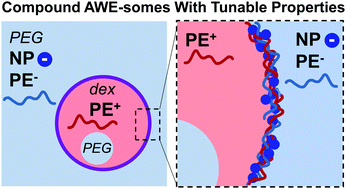
Tuning interfacial complexation in aqueous two phase systems with polyelectrolytes and nanoparticles for compound all water emulsion bodies (AWE-somes)
Compound AWE-somes with tunable shells generated by aqueous interfacial complexation of a polycation with a polyanion and anionic nanoparticle mixture.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23825-23831
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02809A
Pattern transitions in a compressible floating elastic sheet
Compressible thin layers floating on a liquid surface develop wrinkled and folded patterns under lateral pressure.
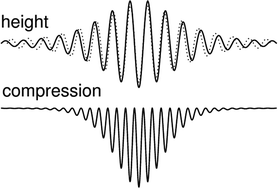
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23817-23824
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03239K
A novel combined chemical kinetic and trapping method for probing the relationships between chemical reactivity and interfacial H2O, Br− and H+ ion molarities in CTAB/C12E6 mixed micelles
Reaction of TBHQ and 16-ArN2+ in CTAB/C12E6 mixed micellar interfaces is strongly affected by the interfacial hydrogen ion concentration and not micelle size.
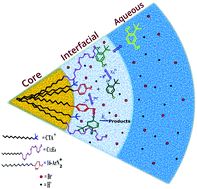
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23747-23761
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP03413J
Swelling of micro-hydrogels with a crosslinker gradient
The swollen structure of microgels with a crosslinked-polymer backbone is recovered by considering the crosslinker gradient inside the particles.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23740-23746
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02434G
Surface cleaning of artworks: structure and dynamics of nanostructured fluids confined in polymeric hydrogel networks
o/w Microemulsion embedded in hydrogels are efficient and safe solvent confinement tools for the cleaning of artworks. The structure of PVA networks and the diffusion properties of a microemulsion are investigated to get fundamental insights on the cleaning processes.
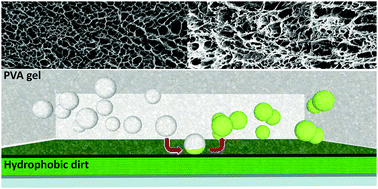
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23762-23772
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02662E
Self-assembled mesoscopic surface domains of fluorocarbon–hydrocarbon diblocks can form at zero surface pressure: tilting of solid-like hydrocarbon moieties compensates for cross-section mismatch with fluorocarbon moieties
Surface domains of C8F17C16H33 exist at zero surface pressure with solid-like alkyl chains stretched in an all-trans configuration, shown using IRRAS.
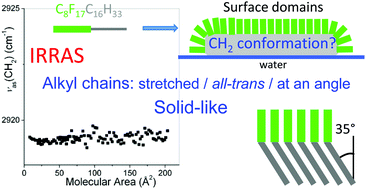
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23809-23816
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02432K
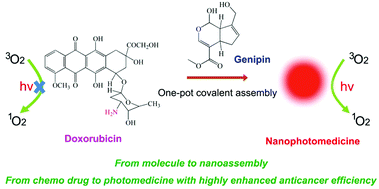
Covalent-reaction-induced interfacial assembly to transform doxorubicin into nanophotomedicine with highly enhanced anticancer efficiency
By one-pot covalent-reaction-induced interfacial assembly, doxorubicin is facilely transformed into nanophotomedicine with remarkable ability of singlet oxygen generation and greatly improved anticancer efficiency.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23733-23739
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02543B
Dewetting acrylic polymer films with water/propylene carbonate/surfactant mixtures – implications for cultural heritage conservation
The surfactant lowers the interfacial energy between the phases, favoring polymer dewetting.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23723-23732
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02608K
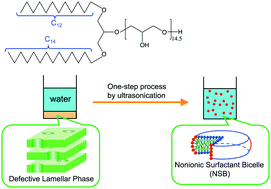
One-step formulation of nonionic surfactant bicelles (NSBs) by a double-tailed polyglycerol-type nonionic surfactant
Bicelles can be formulated by a simple one-step process using a polyglyceryl dialkyl ether that has asymmetric tails.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 23802-23808
https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP02585H
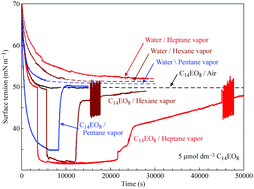
Adsorption of C14EO8 at the interface between its aqueous solution drop and air saturated by different alkanes vapor
The dynamic and equilibrium surface tension for drops of aqueous C14EO8 solutions at the interface to pure air or pentane, hexane, heptane and toluene saturated air, and the dynamic surface tension of pure water at these interfaces are presented.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19, 2193-2200
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CP07705F
About this collection
Guest Editors, Krister Holmberg (Chalmers University of Technology) and Junbai Li (Chinese Academy of Sciences) are delighted to introduce this Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics (PCCP) themed collection dedicated to surface chemistry and interface science. The special issue includes a collection of high quality Communications, Perspectives and full papers to showcase the cutting edge research being undertaken in the subject and illustrate the current state of the art in the field.