Themed collection Mechanical properties of nanoassemblies

Synthesis and mechanical response of disordered colloidal micropillars
A method for synthesizing and uniaxially compressing free-standing colloidal micropillars is presented. The mechanical response of the micropillars is strongly dependent upon their initial defect population and water content.
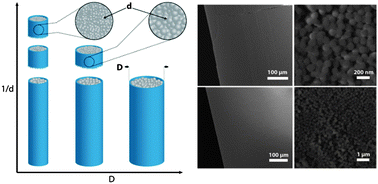
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 10274-10285
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP55422H
Silver nanoparticle aided self-healing of polyelectrolyte multilayers
Weak polyelectrolyte multilayer films containing silver nanoparticles are shown to have enhanced ability to self-heal when exposed to water when compared to the films assembled without particles.
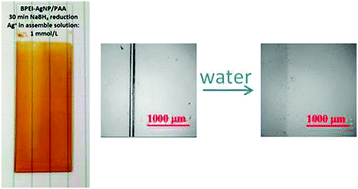
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 10267-10273
https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP00349G
Strain localization in glassy polymers under cylindrical confinement
Glassy polymeric pillars show strain localization during tensile deformation which is absent in pillars cooled two orders of magnitude faster.
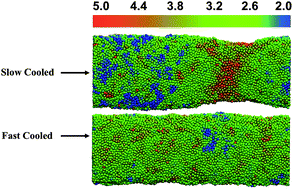
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 10301-10309
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP55330B
Stretching of assembled nanoparticle helical springs
Assembled nanoparticle helical ribbons have impressive mechanical properties that are predictable through surface and elastic energies.
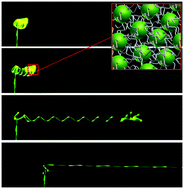
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 10261-10266
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP55502J
Mechanotunable monatomic metal structures at graphene edges
Graphene edge is an efficient one-dimensional template for low-dimensional, mechanotunable metal structures such as chains, rings and helices.

Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 10295-10300
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP55063J
Conformational interchange of a carbohydrate by mechanical compression at the air–water interface
Conformational interchange of a fluorescent-labelled carbohydrate by macroscopic mechanical force.
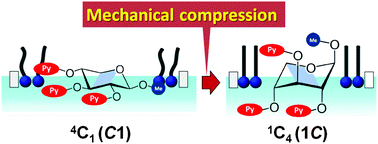
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014,16, 10286-10294
https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CP55078H
About this collection
A collection of articles relating to understanding, controlling and enhancing the mechanical properties of nanoassemblies and nanosystems, guest edited by Daeyeon Lee, University of Pennsylvania.