Themed collection Metal-organic frameworks

MOFs for CO2 capture and separation from flue gas mixtures: the effect of multifunctional sites on their adsorption capacity and selectivity
Understanding the effect of functional sites on the MOF CO2 adsorption capacity and selectivity.
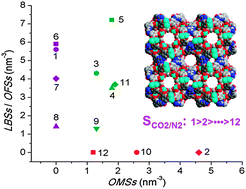
Chem. Commun., 2013,49, 653-661
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC35561B
Commercial metal–organic frameworks as heterogeneous catalysts
Commercially available MOFs can be highly active, reusable catalysts for liquid-phase acid-catalyzed and aerobic oxidation reactions.
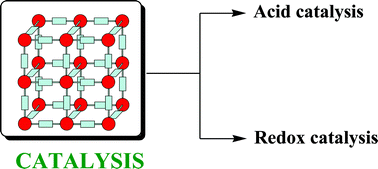
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 11275-11288
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34329K
Single-crystal-to-single-crystal direct cross-linking and photopolymerisation of a discrete Ag(I) complex to give a 1D polycyclobutane coordination polymer
A discrete dinuclear Ag(I) tetrastilbazole undergoes a single-crystal-to-single-crystal reaction to form a 1D polycyclobutane.
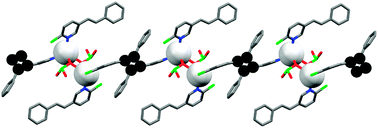
Chem. Commun., 2013,49, 1064-1066
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC36458A
Voltammetric reduction and re-oxidation of solid coordination polymers of dihydroxybenzoquinone
A 2D coordination polymer has been shown to undergo a reversible solid-state to solid-state electrochemical conversion with retention of the network connectivity.

Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 11422-11424
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34687G
Successful implementation of the stepwise layer-by-layer growth of MOF thin films on confined surfaces: mesoporous silica foam as a first case study
Here we report the successful growth of homogenous MOF thin films of HKUST-1 and ZIF-8 on mesoporous silica foam using a layer-by-layer method.
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 11434-11436
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC36233C
Understanding excess uptake maxima for hydrogen adsorption isotherms in frameworks with rht topology
For a series of metal–organic frameworks with rht topology, we study computationally the effect of the linker length on the surface area, pore size, and pore volume, relating them with the hydrogen adsorption properties. The results provide new insights about the excess capacities and the pressures where the uptake maxima in the excess isotherms occur.

Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 10496-10498
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC35711A
Assessing the adsorption selectivity of linker functionalized, moisture-stable metal–organic framework thin films by means of an environment-controlled quartz crystal microbalance
The stepwise deposition of a robust, MOF-5-analogue family as thin films is reported and the selective adsorption of probe molecules onto the films as a function of the linker functionalization is demonstrated.
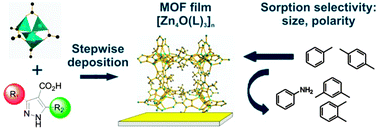
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 10493-10495
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34608G
Control of framework interpenetration for in situ modified hydroxyl functionalised IRMOFs
Phase-pure metal–organic frameworks [Zn4O(L)3] are formed in one-pot reactions with liberation of accessible ‘metal-binding’ groups within the frameworks.
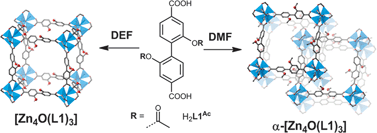
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 10328-10330
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC35565E
Stepwise construction of grid-type Cu(II)–Cd(II) heterometallic MOFs based on an imidazole -appended dipyrrin ligand
An imidazole-appended dipyrrin ligand yields, upon coordination to Cu(II) cations, a linear metallatecton that self-assembles with Cd(II) salts to afford grid-type MOFs which, upon parallel stacking, lead to porous crystals offering 1D channels.
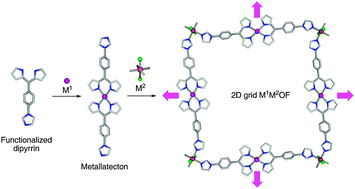
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 10313-10315
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC35543D
A versatile metal–organic framework for carbon dioxide capture and cooperative catalysis
A MOF PCN-124 exhibits selective adsorption of CO2 over CH4 and cooperative catalytic activity in a tandem deacetalization–Knoevenagel condensation reaction.
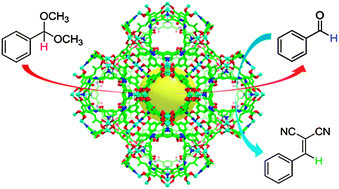
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 9995-9997
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34622B
Non-interpenetrated IRMOF-8: synthesis, activation , and gas sorption
The successful synthesis, activation, and gas sorption properties of phase-pure IRMOF-8 is reported, solving a decade-old puzzle.
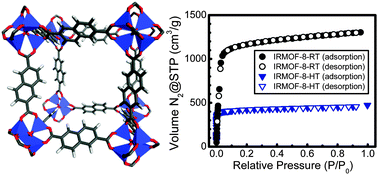
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 9828-9830
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34689C
CH4 storage and CO2 capture in highly porous zirconium oxide based metal–organic frameworks
Thermal, water and mechanical resistant zirconium-based MOF materials with exceptionally high CH4 and CO2 adsorption uptakes.

Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 9831-9833
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34714H
A new Al-MOF based on a unique column-shaped inorganic building unit exhibiting strongly hydrophilic sorption behaviour
A new Al-MOF denoted CAU-6 exhibits infinite column-shaped inorganic building units based on tridecanuclear Al-oxo-clusters and hydrophilic sorption behaviour.
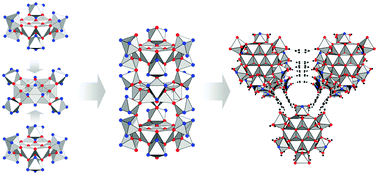
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 9486-9488
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34909D
Functional group effects on metal–organic framework topology
The first functionalized 1,3,5-tris(4-carboxyphenyl)benzene (H3BTB) ligands have been prepared that generate an isostructural, functionalized MOF-177 framework, as well as the novel, interpenetrated pcu-e framework.

Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 9370-9372
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34938H
Zr(IV) and Hf(IV) based metal–organic frameworks with reo-topology
Zr and Hf based MOFs with reo topology showing enhanced pore accessibility for large molecules and high hydrolytic stability were obtained.
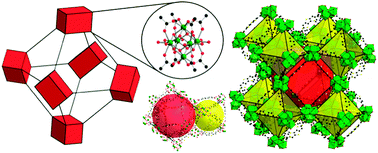
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 8407-8409
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC34246D
Highly emissive Zn–Ln metal–organic frameworks with an unusual 3D inorganic subnetwork
Mixed zinc–lanthanide metal–organic frameworks based on the 3,5-pyrazoledicarboxylate ligand exhibit an unusual three-dimensional inorganic subnetwork and highly efficient photoluminescence.

Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 7964-7966
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC33223J
Porous carbon materials with a controllable surface area synthesized from metal–organic frameworks
Carbonization of zinc containing metal–organic frameworks produces porous carbon materials with an interesting linear relationship between the Zn/C ratio of the precursors and the surface area of the resulting carbon materials.
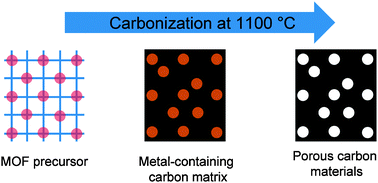
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 7447-7449
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC33439A
Assembly of super-supertetrahedral metal–organic clusters into a hierarchical porous cubic framework
Reported here is a porous framework constructed from super-supertetrahedral metal–organic clusters and exhibiting four hierarchical levels of supramolecular assembly.

Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 7498-7500
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC32907G
Synthetic control of framework zinc purinate crystallisation and properties of a large pore, decorated, mixed-linker RHO-type ZIF
A mixed-linker RHO-type ZIF with Im![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m symmetry and large pore size is one of four new purine-containing frameworks prepared solvothermally.
m symmetry and large pore size is one of four new purine-containing frameworks prepared solvothermally.

Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 6690-6692
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC32927A
Targeted functionalisation of a hierarchically-structured porous coordination polymer crystal enhances its entire function
A post-synthetic modified core–shell crystal of a porous coordination polymer accumulated aniline derivatives and gave the intense exciplex emission.
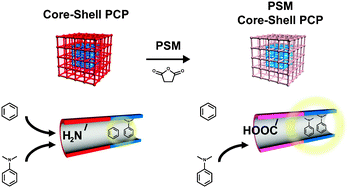
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 6472-6474
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC31421E
Facile synthesis of metal–organic framework films via in situ seeding of nanoparticles
A facile in situ nanoparticle seeding method is reported to prepare MIL-101(Cr) films on alumina supports. The in situ seeding of MIL-101(Cr) nanoparticles was promoted by use of dimethylacetamide. The generality of this approach is further demonstrated for Cu3(btc)2 films by using a (poly)acrylate promoter.
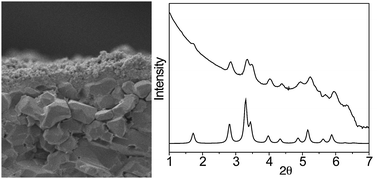
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 4965-4967
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC31079A
Calix[4]arene-based metal–organic frameworks: towards hierarchically porous materials
An upper rim-functionalised calix[4]arene dicarboxylic acid (H2caldc) has been used to prepare four metal–organic frameworks, three of which have been structurally characterised and shown to form two- or three-dimensional network structures.
![Graphical abstract: Calix[4]arene-based metal–organic frameworks: towards hierarchically porous materials](/en/Image/Get?imageInfo.ImageType=GA&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.ManuscriptID=C2CC30988B&imageInfo.ImageIdentifier.Year=2012)
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 4824-4826
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC30988B
Instantaneous gelation of a new copper(II) metallogel amenable to encapsulation of a luminescent lanthanide cluster
We describe a copper(II) containing discrete metal complex gelator able to gel dimethylformamide (DMF) at 0.51 wt%.
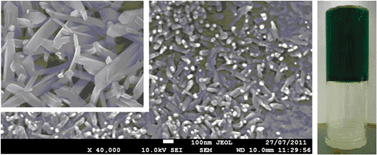
Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 4830-4832
https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC30170A
About this collection
The peer-reviewed articles in this ChemComm web themed issue will highlight recent cutting-edge achievements in the exciting field of metal-organic frameworks.
The guest editors of the issue are Neil Champness (University of Nottingham, UK), Christian Serre (University of Versailles, France) and Seth Cohen (University of California, San Diego, USA).
Articles in this web themed issue will be added below as soon as possible, after they are published.