Regio- and stereo-controlled synthesis of 6-deoxy-β-d-ido-heptopyranosides related to Campylobacter jejuni HS:4†
Abstract
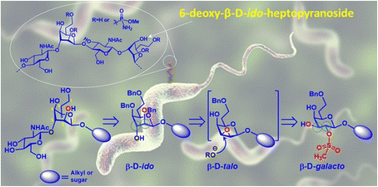
Campylobacter jejuni is a bacterial pathogen that causes hundreds of millions of cases of food-borne gastroenteritis worldwide annually. The infection caused by this bacterium is also associated with several forms of post-infectious autoimmune sequelae that can be very serious, including the life-threatening Guillain-Barré syndrome. The capsular polysaccharides (CPS) of C. jejuni HS:4 consist of a very unique repeating disaccharide unit that is characterized by a β-1,4-linked 6-deoxy-β-D-ido-heptopyranose and an N-acetyl-β-D-glucosamine. Eliciting carbohydrate-specific antibodies against the CPS structures of C. jejuni HS:4 is an attractive strategy. The 6-deoxy-ido-configuration of the heptose combined with its β-anomeric configuration makes the chemical synthesis of the disaccharide very challenging. Here, we report an efficient synthesis to obtain the key repeating disaccharide and its analog in reverse order plus a trisaccharide. Our synthesis features a highly efficient, one-step stereo- and regioselective conversion of β-D-galacto-heptopyranosides to 6-deoxy-β-D-ido-heptopyranosides via the intermediate 2,3-anhydro-β-D-talo-heptopyranosides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...