A nucleophilic addition–elimination based ratiometric fluorescent probe for monitoring N2H4 in biological systems and actual samples†
Abstract
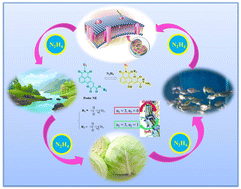
Hydrazine (N2H4) is an important reagent in the field of fine chemical engineering. However, its accumulation in the environment and food chain could pose a great threat to food safety and human health. Therefore, designing a fluorescent probe with good cell penetration and high selectivity and sensitivity to detect N2H4 in actual samples and in vivo is a meaningful project. Herein, due to the nucleophilicity of hydrazine, we utilized naphthalimide as the fluorescence chromophore and pyrone as the recognition site to achieve the ratiometric detection of hydrazine by ring opening. In addition, we introduced the ester to improve the lipid solubility of the probe, which allowed the probe to better penetrate the cell membrane to realize the fluorescent imaging of probes in cells. Meanwhile, to our delight, the probe showed high selectivity and sensitivity to N2H4 in the test system, so we further applied the probe in water samples and food, in vitro and in vivo.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst HOT Articles 2023


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...