Development of a single-step fluorogenic sirtuin assay and its applications for high-throughput screening†
Abstract
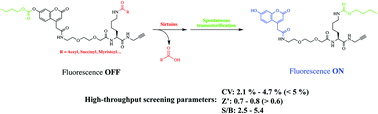
Sirtuins (SIRTs) are a class of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-dependent histone deacetylases. Since SIRTs have different subcellular locations and different preferences for deacylation activity, SIRTs are not only highly gaining significance in biological functions but also implications in human diseases. Therefore, it is valuable to establish a high-throughput screening method for the rapid and accurate discovery of SIRT modulators. In this study, we designed and synthesized small molecules 4a–d as fluorogenic probes based on the different lysine substrates of SIRTs, which can be recognized and catalyzed by SIRTs and then spontaneous intramolecular transesterification can give the fluorescence. We have undertaken a comprehensive study of these fluorogenic probes with different SIRTs for assay optimization, validation, kinetics, parameters, and applications of high-throughput screening formats. We envision that these probes will provide useful and powerful tools for the highly efficient discovery of more SIRT inhibitors.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...