Design and computational insight into two novel CL-20 analogues, BNMTNIW and BNIMTNIW: high performance energetic materials†
Abstract
In this study, a theoretical insight into two newly designed novel CL-20 based high performance energetic compounds, namely bis(nitromethyl)-tetranitrohexaaza-isowurtzitane (BNMTNIW) and bis(nitratomethyl)-tetranitrohexaaza-isowurtzitane BNIMTNIW), is reported. The title compounds are expected to exhibit good densities, 2.05 g cm−3 and 1.98 g cm−3, respectively, and high positive enthalpies of formation 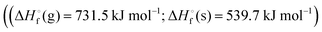 and
and 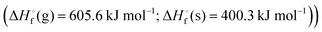 and excellent detonation performance (DP = 44.18 and 41.42 GPa, Dv = 9735 and 9460 m sec−1), respectively. Computed bond dissociation energies (BDEs) and impact sensitivities (IS) suggest that these molecules are more stable than 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane (HNIW, CL-20). We also propose a synthetic strategy for the preparation of BNMTNIW and BNIMTNIW from a commercially available starting material, glyoxal. IR and Raman spectra of BNMTNIW and BNIMTNIW are predicted. These attractive propulsive and explosive properties and better thermal stability and sensitivity than CL-20 (HNIW) suggest the great potential of the title compounds as high energy density materials.
and excellent detonation performance (DP = 44.18 and 41.42 GPa, Dv = 9735 and 9460 m sec−1), respectively. Computed bond dissociation energies (BDEs) and impact sensitivities (IS) suggest that these molecules are more stable than 2,4,6,8,10,12-hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane (HNIW, CL-20). We also propose a synthetic strategy for the preparation of BNMTNIW and BNIMTNIW from a commercially available starting material, glyoxal. IR and Raman spectra of BNMTNIW and BNIMTNIW are predicted. These attractive propulsive and explosive properties and better thermal stability and sensitivity than CL-20 (HNIW) suggest the great potential of the title compounds as high energy density materials.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...