Effective removal of Cd(ii) by sludge biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron from aqueous solution: characterization, adsorption properties and mechanism
Abstract
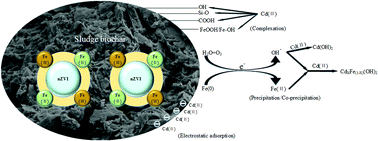
Nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) has a high chemical reactivity for heavy metals, but it forms aggregates easily. In this study, a synthesis of sludge biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI@SBC) by the liquid-phase reduction method can effectively overcome this problem and shows good potential to remove Cd(II) in an aqueous solution. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images showed that sludge biochar (SBC) as a stable carrier could effectively prevent the aggregation of nZVI, and only some particles were chain-shaped. EDS analysis showed that the iron content on the SBC surface increased from 9.76% to 66.91% after loading of nZVI. The maximum adsorption of Cd(II) by nZVI@SBC (149.67 mg g−1) could be achieved at 298 K and pH = 5.0 ± 0.2, which indicated that nZVI@SBC had a good effect on the removal of Cd(II). The pseudo-second-order kinetic model could more accurately explain the removal kinetics. The Freundlich adsorption isotherm model could well fit the adsorption process. Adsorption thermodynamics showed that the adsorption process was a spontaneous endothermic reaction. The presence of Ca(II) and Mg(II) in the solution strongly inhibited the removal of Cd(II), while HA had no significant effect. The removal mechanism of Cd(II) by nZVI@SBC obtained from SEM-EDS, BET, XRD, FTIR and XPS included electrostatic adsorption, precipitation/co-precipitation and the formation of complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...