p-Synephrine suppresses inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and alleviates systemic inflammatory response syndrome in mice†
Abstract
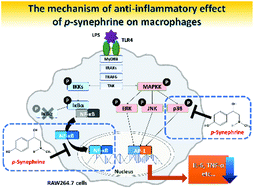
p-Synephrine is the primary protoalkaloid found in Citrus species such as Citrus aurantium (bitter orange) and is widely used as a dietary supplement. Although studies have shown the anti-inflammatory effect of p-synephrine, the cells targeted and detailed mechanism(s) of action are not established. Therefore, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of p-synephrine and elucidated its underlying mechanisms in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, peritoneal macrophages, and an LPS-induced systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) mouse model. We found that p-synephrine inhibits the production of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, and proinflammatory cytokines in primary peritoneal macrophages. This effect of p-synephrine is due to downregulation of the p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway and is mediated by β-adrenergic receptors. Oral administration of p-synephrine to SIRS mice inhibited the serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines and improved their survival rate. Thus, our findings show that p-synephrine alleviates the hyperinflammatory response in macrophages and a SIRS mouse model.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...