Harnessing the toxicity of dysregulated iron uptake for killing Staphylococcus aureus: reality or mirage?†
Abstract
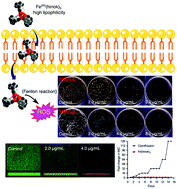
Iron is essential for all forms of life including pathogenic bacteria. However, iron is also a double-edged sword in biology, as increase of iron uptake can result in reactive oxygen species (ROS)-triggered cell death from the iron-catalyzed Fenton reaction. In this study, we demonstrate that iron-hinokitiol, Fe(hinok)3, a neutral Fe(III) complex formed with the naturally occurring metal chelator hinokitiol; (2-hydroxy-4-isopropyl-2,4,6-cycloheptatrien-1-one) can harness the clear ability, due to its high lipophilicity and the nonpolar nature, to penetrate the cell membrane of Staphylococcus aureus (SA) and exhibit potent antimicrobial activity that is enhanced by approximately 10 000 times as compared with hinokitiol itself. Additionally, this Fe(III) complex shows a strong ability to inhibit biofilm formation. More importantly, the development of resistance in SA toward this complex is considerably hampered in comparison with that toward ciprofloxacin. The in vivo evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy in the murine model of skin wound infection by SA confirms that the treatment with a single dose of this complex can reduce the bacterial burden by 83%, demonstrating the therapeutic potential of Fe(hinok)3 in treating skin and soft tissue infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...