pH-Responsive expandable polycarbonate–doxorubicin conjugate nanoparticles for fast intracellular drug release†
Abstract
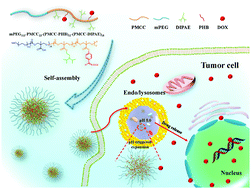
Nanoparticles used as drug carriers that have a prolonged circulation time, reduced early drug leakage, being stimulus triggered and having an improved drug release are a powerful tool for anticancer treatment. Herein, a new tailor-made polycarbonate–doxorubicin conjugate was prepared and characterized, in which the aliphatic polycarbonate was functionalized with tertiary amine groups, and an acid-sensitive benzoic imine bond was formed between doxorubicin (DOX) and the polycarbonate. The conjugate could self-assemble into nanoparticles (DOX–P1 NPs) with a size of 49 nm and an initial negative surface charge. Furthermore, DOX–P1 NPs possess a high drug-loading of 18.3% and exhibit pH-dependent drug-release behavior. As anticipated, DOX–P1 NPs show good stability and can avoid early drug leakage during circulation in vivo. However, after endocytosis, the nanoparticle size expanded rapidly to 65 nm, allowing the maximized exposure of the benzoic imine bond and achieving fast intracellular drug release. In addition, in vitro cytotoxicity studies demonstrate a remarkable tumor inhibition of the DOX–P1 NPs against 4T1 cells. Consequently, these intracellular pH-responsive expandable nanoparticles have great potential for safe and effective drug delivery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...