Constructing a bacterial cellulose-based bacterial sensor platform by enhancing cell affinity via a surface-exposed carbohydrate binding module†
Abstract
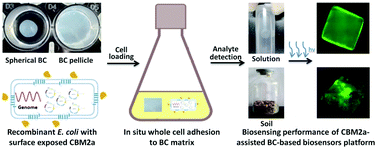
The use of fluorescence-based bacterial sensors requires the tethering of live bacterial sensors to a materials platform while preserving the biological activity of the cells. Herein, we present a proof of concept for designing a bacterial cellulose (BC)-based bacterial sensor platform via a CBM2a-assisted cell adhesion strategy. By placing CBM2a on the cell surface, efficient and specific immobilization of recombinant E. coli to the BC matrix, without any substrate modification, was achieved. Compared with a BC carrier loaded with pristine E. coli cells, cells with surface-exposed CBM2a bind tightly to BC carriers even after 60 h of incubation under external shear forces. Evaluation of the biosensing performance of the BC-based biosensor platform using a constructed L-arabinose inducible biosensor model showed that the CBM2a-assisted BC-based biosensor platform sensitively detects arabinose in either aqueous solution or mixed with soil, resulting in distinguishable fluorescence output of the BC carriers. These results prove that a surface-exposed CBM2a approach is a convenient and effective way of enhancing cell affinity for a BC matrix, and also demonstrate the potential of using CBM2a as an affinity tag in designing a cellulose-based biosensing platform.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...