Effect of d-allulose feeding on the hepatic metabolomics profile in male Wistar rats
Abstract
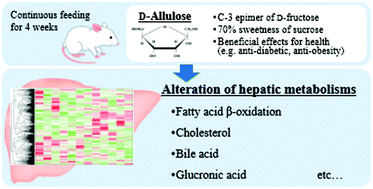
The rare sugar D-allulose is a C-3 epimer of D-fructose and is known to have several health benefits such as anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects through the alteration of enzymatic and genetic expressions in each organ. Most of the ingested D-allulose is absorbed in the small intestine and then rapidly excreted in the urine. As D-allulose was reported to be present in the liver before it is excreted, D-allulose may modulate some hepatic metabolites including glucose and lipid metabolism. Therefore, we investigated the hepatic metabolomics profile in rats after feeding D-allulose to study the overall alteration of hepatic metabolism. Wistar rats were fed an AIN-93G diet with/without 3% D-allulose for 4 weeks. Their liver samples were then collected and subjected to metabolomics analysis using CE-TOFMS and LC-TOFMS. The results showed that D-allulose induced significant increases in 42 metabolites and significant decreases in 21 metabolites. In particular, we found at the substance levels that D-allulose regulated metabolites involved in the metabolic pathways of fatty acid β-oxidation, cholesterol, and bile acid. In addition, this study newly showed the possibility that D-allulose alters glucuronic acid/xylulose pathways. In the future, we need more detailed research on the metabolomics profile of other organs related to these pathways for a comprehensive understanding of D-allulose functions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...