Nitrate reduction to ammonium: from CuO defect engineering to waste NOx-to-NH3 economic feasibility†
Abstract
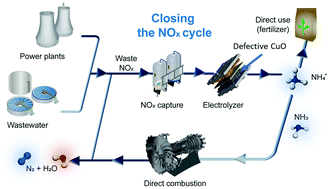
Critical to the feasibility of electrochemical reduction of waste NOx (NOxRR), as a sustainable pathway and to close the NOx cycle for the emerging NH3 economy, is the requirement of inexpensive, scalable and selective catalysts that can generate NH4+ with high yield, as indicated by our economic modelling. To this end, we carry out density functional theory (DFT) calculations to investigate the possible contribution of oxygen vacancy (OV) defects in NOxRR catalysis, discovering that an increase in defect density within CuO is leading to a decrease in adsorption energy for NO3− reactants. Using these findings as design guidelines, we develop defective CuO nanomaterials using flame spray pyrolysis (FSP) and mild plasma treatment, that can attain a NH4+ yield of 520 μmol cm−2 h−1 at a cell voltage of 2.2 V within a flow electrolyser with good stability over 10 h of operation. Through our mechanistic investigation, we establish the beneficial role of oxygen vacancy defects (with one free electron) in CuO for NOxRR and we reveal a direct correlation of oxygen vacancy density with the NH4+ yield, arising from improved NO3− adsorption, as evidenced from our theoretical calculations. Our findings on defect engineering to improve NH4+ yield and its economic feasibility display the potential of NOxRR as an alternative pathway to generate green NH3, which can also serve as an energy vector for the emerging hydrogen economy and close the NOx cycle.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...