Evaluation of the role of the DNA surface for enhancing the activity of scaffolded enzymes†
Abstract
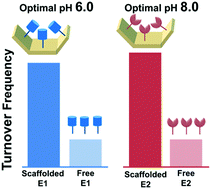
The catalytic enhancements of enzymes loaded on DNA nanostructures have been attributed to the characteristics provided by highly negative charges on the surface of the DNA scaffold, such as the modulation of the local pH near enzymes. In this study, two types of enzymes with optimal activity at pH 6 and 8 equally displayed significant catalytic enhancements on the DNA scaffold surface. By using a ratiometric pH indicator, a lower local pH shift of 0.8 was observed near the DNA scaffold surface. The postulated local pH change near the DNA scaffold surface is unlikely to play a general role in enhancing the activity of the scaffolded enzymes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
