Anion binding and fluoride ion induced conformational changes in bisurea receptors†
Abstract
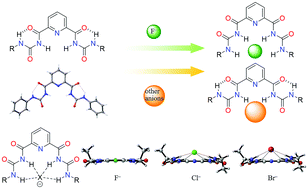
Two types of bisurea receptors, containing either 2,6-substituted phenyl or 2,6-substituted pyridine, are prepared, and their anion binding properties are investigated. Compared with the phenyl bisurea receptors, the pyridine bisurea receptors can be more easily converted to a cis–cis conformation from a trans–trans conformation, providing a cavity that more closely matches the volume of a fluoride ion and increasing the number of NH sites bound to the fluoride ion. As a result, the pyridine bisurea in cis–cis conformation shows stronger affinity and higher selectivity to fluoride ions, which is supported by crystal structure analysis and NMR titration experiments. Through DFT calculations, a mechanism of fluoride ion induced conformational changes of pyridine bisurea receptors is proposed, and the energy barriers of conformational changes for both types of receptors are determined.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...