Lactobacillus casei LC2W can inhibit the colonization of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in vivo and reduce the severity of colitis
Abstract
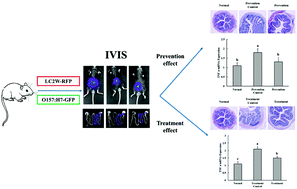
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) is a strain of human pathogenic E. coli bacteria that can cause serious foodborne diseases. Many probiotics have antagonistic effects on EHEC, but few studies have examined the interactions between probiotics and EHEC in vivo. To investigate the colonization of Lactobacillus casei LC2W and its inhibitory effect on E. coli O157:H7 in vivo, these strains labelled with different fluorescent proteins were monitored in the intestinal tracts of live mice using an in vivo imaging system. The results showed that L. casei LC2W inhibited the colonization of O157:H7 in mice. Further research found that LC2W had both prevention and treatment effects on the colitis severity of mice infected by O157:H7, where the prevention effect dominated over the treatment one. This study demonstrates a feasible method for studying the interactions between probiotics and pathogens, and the mechanisms by which probiotics reduce colitis induced by O157:H7.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...