The green poly-lysine enantiomers as electron-extraction layers for high performance organic photovoltaics†
Abstract
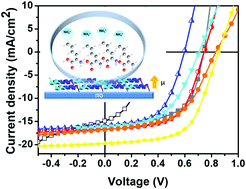
In this study, we first revealed green materials – poly-lysines (poly-L-lysine and poly-L-lysine blend poly-D-lysine) – as electron-extraction layers (EELs) in organic photovoltaics (OPVs). The distinct configurations of poly-lysine enantiomers were verified by conducting zeta potential analysis, and their work function (WF)-tuning capabilities for indium tin oxide (ITO) were affirmed by ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS). These two poly-lysine groups, with different arrangements of the amino groups that built up different surface dipoles on the ITO substrate, altered the surface energy and WF of ITO. Poly-L-lysine optimized the WF of ITO for efficient carrier transport in the OPV device, in the electron transporting layer-free OPV devices, and we observed a high power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 10.01% in the device configuration of ITO/interlayer/BHJ/MoO3/Ag. As the first examination of poly-lysine enantiomers for OPVs, we provided the WF-tuning functions – increasing polarity as an interfacial dipole is formed at the corresponding interface, and discovered a promising interfacial material possessing high efficiency and benefitting from a long-term stability to perform in a stable PCE with about 80% of its original PCE remaining after continuous heat and light treatment for 400 hours.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...