The inverted solvatochromism of protonated ferrocenylethenyl-pyrimidines: the first example of the solvatochromic reversal of a hybrid organic/inorganic dye†
Abstract
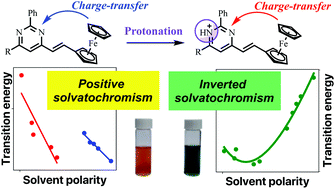
Five new solvatochromic 2,6-diaryl-4-ferrocenylethenylpyrimidines were synthesized and their spectral variations in solution investigated in twenty-seven solvents of variable polarity. Their observed positive solvatochromism in HBD- and non-HBD-solvents changed to an inverted behavior upon protonation of the pyrimidine ring by the addition of trifluoroacetic acid. Multiparametric analysis of the solvatochromic band of the protonated dyes showed that the solvent acidity and polarizability were mainly responsible for their inverted behavior, which arose from an internal charge-transfer from the ferrocene fragment to the pyrimidinium acceptor, confirmed by theoretical calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...