Electrochemical detection of an antibiotic drug chloramphenicol based on a graphene oxide/hierarchical zinc oxide nanocomposite
Abstract
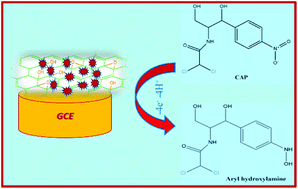
A novel electrochemical sensor based on a graphene oxide (GO)/three-dimensional (3D) hierarchical zinc oxide (ZnO) nanocomposite was developed for the efficient determination of the antibiotic drug chloramphenicol (CAP). The hierarchical ZnO structure consisting of nanosheets was synthesized by a green aqueous solution procedure and then composited with GO through a simple sonochemical method. The synthesized ZnO and GO/ZnO nanomaterials were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), elemental mapping, X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV-Visible spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and Raman spectroscopy. The electrochemical performance of the prepared GO/ZnO/glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was evaluated using cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) techniques. The GO/ZnO/GCE shows a low CAP detection limit of 0.01 μM, a high sensitivity of 7.27 μA μM−1 cm−2, and a linear response in the range of 0.2 to 7.2 μM. Moreover, it exhibits excellent stability, reproducibility and repeatability. Practicality of the sensor has further been demonstrated with honey, milk and eye drop samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...