A flower-structured MoS2-decorated f-MWCNTs/ZnO hybrid nanocomposite-modified sensor for the selective electrochemical detection of vitamin C
Abstract
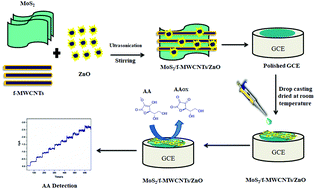
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C, AA) is an important vitamin and essential component in the human diet. However, an unusual level of AA is generally a symptom of illness, and thus, the development of sensitive and selective detection methods for its biological analysis is important. Herein, we developed a new electrochemical sensor for the highly selective detection of AA using flower-structured molybdenum disulfide (MoS2)-decorated functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes (f-MWCNTs)/zinc oxide (ZnO). The flower-structured MoS2 and ZnO nanoflakes were synthesized by hydrothermal and microwave-assisted solution methods, respectively. The surface morphology, particle size and elemental/chemical composition of the as-synthesized MoS2/f-MWCNTs/ZnO nanocomposite were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDXS). Furthermore, the electrochemical properties of the MoS2/f-MWCNTs/ZnO nanocomposite were studied by cyclic voltammetry (CV). The MoS2/f-MWCNTs/ZnO-modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE) exhibited a high catalytic current for AA at a reduced overpotential in a 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (PBS). The MoS2/f-MWCNTs/ZnO/GCE responded linearly from 10 to 100 μM AA at 0.21 V, and its limit of detection (LOD) was found to be 1.65 μM. In addition, the MoS2/f-MWCNTs/ZnO sensor offered fast electron transfer, good anti-interferent ability and stable response for AA sensing. The good solubility of f-MWCNTs in water was beneficial for the formation of the nanocomposite with MoS2 and ZnO via carboxyl groups, which created numerous catalytic centers to oxidize AA efficiently. This nanocomposite also blocked the adsorption of other species on the surface of the modified GCE. The proposed sensor offers high accuracy, sensitivity, simple fabrication and low cost. Finally, the MoS2/f-MWCNTs/ZnO nanocomposite sensor was used for AA analysis in real samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...