Comparative genomics and transcriptomics insights into the C1 metabolic model of a formaldehyde-degrading strain Methylobacterium sp. XJLW†
Abstract
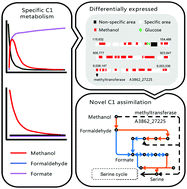
A formaldehyde-degrading strain Methylobacterium sp. XJLW was isolated and exhibited a special phenotype for formaldehyde utilization. The accumulation of formic acid in large quantities and lower cell growth was detected when XJLW utilized formaldehyde as the sole carbon source, suggesting XJLW has a potentially novel pathway to transfer formaldehyde to methanol and then enter the serine cycle for C1 metabolism. This mechanism requires exploration via molecular omics. Thus, the complete genome of XJLW was sequenced, and the transcriptome difference was also analyzed based on the RNA-seq data of strain XJLW cultivated with methanol and glucose, respectively. XJLW has a chromosome DNA and a mega-plasmid DNA. Ten percent of genes on chromosome DNA are strain-specific in genus Methylobacterium. Transcriptome analysis results showed that 623 genes were significantly up-regulated and that 207 genes were significantly down-regulated for growth in methanol. Among the up-regulated genes, 90 genes belong to strain-specific regions and are densely distributed in three areas. A specific gene (A3862_27225) annotated as methyltransferase was found ranking in the top 4 of up-regulated genes. This methyltransferase may play a role in the specific C1 metabolism of XJLW. Methylobacterium sp. XJLW should contain a potential methyl transport pathway via the novel methyltransferase, which is different from known pathways. These findings provide the basis for additional possibilities, which improve the formaldehyde-degrading ability of Methylobacterium sp. XJLW.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...