Early detection of E. coli and total coliform using an automated, colorimetric and fluorometric fiber optics-based device†
Abstract
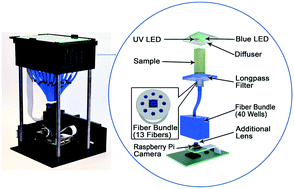
Lack of access to clean water is a major global issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Drinking contaminated water can be extremely hazardous, so it is imperative that it is tested sufficiently. One method commonly used to determine the quality of water is testing for both E. coli and total coliform. Here, we present a cost-effective and automated device which can concurrently test drinking water samples for both E. coli and total coliform using an EPA-approved reagent. Equipped with a Raspberry Pi microcontroller and camera, we perform automated periodic measurements of both the absorption and fluorescence of the water under test over 24 hours. In each test, 100 mL of the water sample is split into a custom designed 40-well plate, where the transmitted blue light and the fluorescent light (under UV excitation) are collected by 520 individual optical fibers. Images of these fiber outputs are then acquired periodically, and digitally processed to determine the presence of the bacteria in each well of the 40-well plate. We demonstrate that this cost-effective device, weighing 1.66 kg, can automatically detect the presence of both E. coli and total coliform in drinking water within ∼16 hours, down to a level of one colony-forming unit (CFU) per 100 mL. Furthermore, due to its automated analysis, this approach is also more sensitive than a manual count performed by an expert, reducing the time needed to determine whether the water under test is safe to drink or not.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
