Optical nano-agents in the second near-infrared window for biomedical applications
Abstract
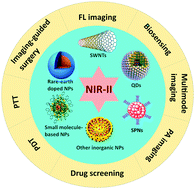
The optical technology presents non-invasive, non-destructive, and non-ionizing features and has the ability to display various chemical components in tissues to provide useful information for various biomedical applications. Regarding selection of light wavelengths, second near-infrared (NIR-II, 900–1700 nm) light is a much better choice compared to both visible (380–780 nm) and traditional near-infrared (780–900 nm) light, because of its advantages including deeper penetration into biological tissues, less tissue scattering or absorption, and decreased interference by fluorescent proteins. Thus, using optical nano-agents that absorb or emit light in the NIR-II window can achieve deeper tissue optical imaging with higher signal-to-background ratios and better spatial resolution for diagnosis. What's more, some of these nano-agents can be further applied for imaging guided surgical removal, real-time monitoring of drug delivery, labeling lymphatic metastasis, biosensing, and imaging guided phototherapy. In this review, we attempt to summarize the recent advances of various NIR-II nano-agents (including single-walled carbon nanotubes, quantum dots, rare-earth doped nanoparticles, other inorganic nanomaterials, small organic molecule-based nanoparticles, and semiconducting polymer nanoparticles) in both bioimaging and therapeutic applications, and discuss the challenges and perspectives of these nano-agents for clinical practice in the near future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...