Homochiral iron(ii)-based metal–organic nanotubes: metamagnetism and selective nitric oxide adsorption in a confined channel†
Abstract
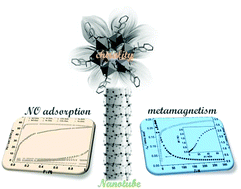
Homochiral iron(II)-based nanotubular metal phosphonates (R)- and (S)-[Fe(pemp)(H2O)2] [pemp2− = (R)- or (S)-(1-phenylethylamino)methylphosphonate] are reported showing metamagnetism at low temperature. The dehydrated product features coordinatively unsaturated and redox-active metal ion sites that enable it to strongly bind nitric oxide at room temperature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...