Effect of the calcination process on CdO–ZnO nanocomposites by a honey-assisted combustion method for antimicrobial performance
Abstract
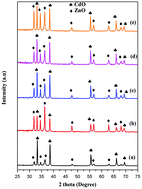
This work reports on honey as a combustion agent of CdO : ZnO nanocomposites and the effects of further annealing (100 °C, 200 °C, 300 °C and 400 °C) on their structural, optical, morphological, elemental, electrical and antimicrobial properties are investigated. X-ray diffraction spectra confirm the cubic and hexagonal structure of CdO : ZnO nanocomposites at 400 °C. When the calcination temperature was increased, the crystallinity, absorbance, bandgap, luminescence intensity, morphological dispersion and mean particle size were also increased. HR-TEM imaging confirmed spherical particles with an average particle size of ∼49 nm. The electrical conductivity of the CdO : ZnO nanoparticles was investigated. The antimicrobial activity of CdO : ZnO nanocomposites was tested for various bacterial and fungal organisms using a zone inhibition method.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Toxicology Research Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...