Intramolecularly enhanced molecular tweezers with unusually strong binding for aromatic guests in unfavorable solvents†
Abstract
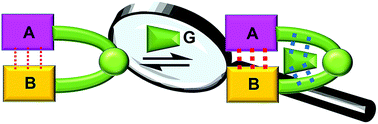
Molecular tweezers using aromatic interactions for binding normally work best in polar instead of nonpolar solvents due to the strong solvophobic effect in the binding. Inspired by biological receptors that utilize “delocalized binding interactions” remote from the binding interface to strengthen guest-binding, we constructed molecular tweezers that have a reversed solvent effect. As the direct aromatic binding interactions were weakened by nonpolar solvent, guest-triggered intrahost interactions between two strategically placed carboxylic acids became stronger and contributed to the binding.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Supramolecular chemistry in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
