Contiguous hydrophobic and charged surface patches in short helix-constrained peptides drive cell permeability†
Abstract
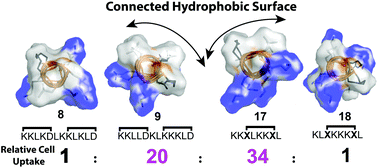
Most protein–protein interactions occur inside cells. Peptides can inhibit protein–protein interactions but tend not to enter cells. We systematically compare cell permeability for 8–12 residue model peptides with helix-inducing lactam/hydrocarbon linkers between amino acid sidechains. Cell uptake increases when hydrophobic residues and lactam linkers (i, i + 4) form a contiguous hydrophobic surface patch. Uptake increases further when both hydrophobic and positively charged (but not neutral or negative) residues are clustered into like surface patches. Amphipathicity alone is however insufficient for cell uptake of acyclic sequences. Changing the linker from lactam to hydrocarbon further increases uptake, but also promotes cell lysis. Helicity, positive charge and amphipathicity together promote cell permeability. Most known bioactive helical peptides do not optimally cluster residues for amphipathicity and so are likely unoptimised for cell uptake.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...