Atomic layer oxidation on graphene sheets for tuning their oxidation levels, electrical conductivities, and band gaps†
Abstract
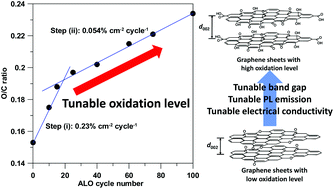
Graphene sheets that can exhibit electrical conducting and semiconducting properties are highly desirable and have potential applications in fiber communications, photodetectors, solar cells, semiconductors, and broadband modulators. However, there is currently no efficient method that is able to tune the band gap of graphene sheets. This work adopts an efficient atomic layer oxidation (ALO) technique to cyclically increase the oxidation level of graphene sheets, thus, tuning their electrical conductance, band-gap structure, and photoluminescence (PL) response. The O/C atomic ratio as an increasing function of the ALO cycle number reflects two linear regions: 0.23% per cm2 per cycle (0–15 cycles) and 0.054% per cm2 per cycle (15–100 cycles). The excellent correlation coefficients reveal that the ALO process follows a self-limiting route to step-by-step oxidize graphene layers. The interlayer distance of ALO-graphene sheets shows an obvious increase after the ALO treatment, proved by X-ray diffraction. As analyzed by X-ray photon spectroscopy, the hydroxyl or epoxy group acts as a major contributor to the interlayer spacing distance and oxidation extent in the initial ALO stage, as compared to carbonyl and carboxyl groups. The ALO mechanism, based on Langmuir–Hinshelwood and Eley–Rideal models, is proposed to clarify the formation of oxygen functionalities and structural transformation from pristine graphene sheets to oxidized ones during the ALO cycle. With a tunable oxidation level, the electrical resistivity, semiconductor character, and PL response of ALO-graphene samples can be systematically controlled for desired applications. The ALO approach is capable of offering a straightforward route to tune the oxidation level of graphene sheets or other carbons.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Nanoscale HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...