Overlayer induced air gap acting as a responsivity amplifier for majority carrier graphene–insulator–silicon photodetectors†
Abstract
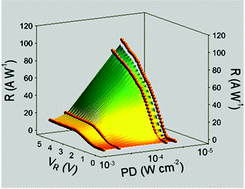
Majority carrier graphene–insulator–silicon (GIS) photodetectors act as photocurrent amplifiers and thus have high potential for various future electro-optic applications requiring their high responsivity, low dark current, high on–off ratio and high detectivity. Further, this study shows that the poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) overlayer on graphene of the majority carrier GIS photodiodes causes more than tenfold enhancement of the known photo-responsivities from the previously reported majority carrier GIS photodiodes. The PMMA overlayer on graphene is acting as not only a graphene protection layer, but also a hole dopant for graphene and a mechanically stiffer layer allowing an air gap formation between graphene and silicon. These collectively provide another route for the photocurrent amplification of the majority carrier GIS photodetectors. As a result, the GIS diode with PMMA shows a responsivity of 95 A W−1 and a detectivity of 2.1 × 1012 cm Hz1/2 W−1 at an optical power density of 35 μW cm−2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...