Metal organic framework-derived CoZn alloy/N-doped porous carbon nanocomposites: tunable surface area and electromagnetic wave absorption properties†
Abstract
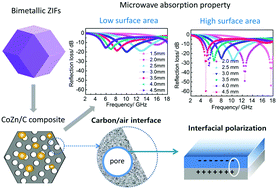
N-Doped porous carbon with uniformly dispersed CoZn alloy nanoparticles has been synthesized through the pyrolysis of a bimetallic zeolitic imidazolate framework containing Zn and Co elements. The surface area, pore size distribution and graphitization of the composites can be modulated easily through changing the molar ratio of Zn to Co in the zeolitic imidazolate framework. Upon increasing the Zn content, the level of graphitization drops gradually and the surface area first increases and then decreases. The increased surface area results in the enhancement of dielectric loss and impedance matching. The sample with a Zn to Co molar ratio of 0.2 in its precursor has the most prominent electromagnetic wave absorption properties, due to appropriate surface area and graphitization properties. The minimum reflection loss reaches −59.7 dB and the widest bandwidth is up to 5.3 GHz. The composites can be good candidates for electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding applications, considering their outstanding performance and simple synthesis route. This study not only offers a simple and facile method for improving dielectric loss and impedance matching of carbon materials, but also sheds light on a new strategy for constructing porous structures, especially porous carbon.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...