Solvent treatment: the formation mechanism of advanced porous membranes for flow batteries†
Abstract
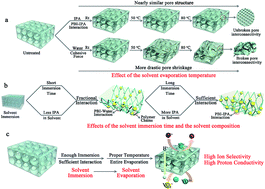
Solvent treatment has been proved to be a very simple and efficient method to prepare high-performance porous membranes for flow batteries. In this article, the process parameters of solvent treatment were regulated to further investigate the formation mechanism of porous membranes. The effect of the solvent evaporation temperature, the solvent immersion time and the solvent composition on the morphology and performance of porous membranes was studied systematically. The adjustment of these process parameters made the acting mechanisms of the polymer–solvent interaction and the cohesive force of polymers more clear. The factors affecting the polymer–solvent interaction and the cohesive force, along with the acting principles of process parameters, were also elucidated in detail. The formation mechanism of porous membranes during solvent treatment was accordingly clarified distinctly. As a result, an optimized VFB performance of treated membranes with a coulombic efficiency of 98.33%, and an energy efficiency of 81.17% at 160 mA cm−2 was achieved, which was much higher than that of Nafion 115 and among the highest values ever reported. Moreover, this VFB could continually run over 2600 cycles at 200 mA cm−2, without obvious efficiency fade. Thus, this paper provides a simpler, quicker and more economical method to prepare high-performance porous membranes for flow batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...