Designing a reductive hybrid membrane to selectively capture noble metallic ions during oil/water emulsion separation with further function enhancement†
Abstract
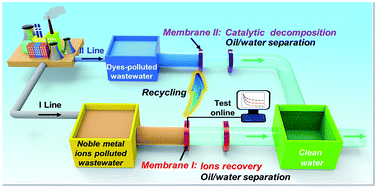
Owing to the ever-increasing demand for noble metals in modern industry, the extraction of noble metals from ores and electronic wastes is a significant topic. Conventional extraction means involving surfactants, organic solvents, and toxic extracting agents suffer from the limitation of complex heterogeneous separation and extraction operation as well as environmental pollution. Herein, a new carbon nanotube (CNT) hybrid membrane modified with eco-friendly and reductive poly acryloyl hydrazide (PAH) is reported, integrating the extraction of noble metal ions with heterogeneous emulsion separation. The hybrid membrane with underwater superoleophobic surface can achieve one-step preferential extraction of noble metal ions during oil/water emulsion separation, greatly simplifying the extraction operation. The reductive extraction yields nanoparticles loaded in situ on CNTs, which allows precise evaluation of the recovery performances by monitoring resistance variation of the hybrid membrane. Furthermore, the extracted hybrid membrane can be recycled for the catalytic conversion of organic contaminants as well as emulsion separation. The multi-functional hybrid membrane realizes comprehensive recovery of noble metal ions and heterogeneous separation for further recycling utilization, showing great potential for practical application towards the simple and integrated recycling of noble metals.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...