Direct measurements of the temperature, depth and processing dependence of phenyl ring dynamics in polystyrene thin films by β-detected NMR
Abstract
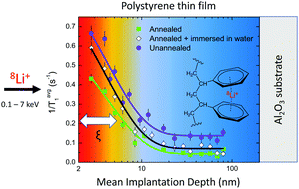
There is indirect evidence that the dynamics of a polymer near a free surface are enhanced compared with the bulk but there are few studies of how dynamics varies with depth. β-Detected nuclear spin relaxation of implanted 8Li+ has been used to directly probe the temperature and depth dependence of the γ-relaxation mode, which is due to phenyl rings undergoing restricted rotation, in thin films of atactic deuterated polystyrene (PS-d8) and determine how the depth dependence of dynamics is affected by sample processing, such as annealing, floating on water and the inclusion of a surfactant, and by the presence of a buried interface. The activation energy for the γ-relaxation process is lower near the free surface. Annealing the PS-d8 films and then immersing in water to mimic the floating procedure used to transfer films had negligible effects on the thickness of the region near the free surface with enhanced mobility. Measurements on a bilayer film indicate enhanced phenyl ring dynamics near the buried interface compared with a single film at the same depth. PS-d8 films annealed with the surfactant sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) deposited on the surface show enhanced dynamics in the bulk compared with a pure PS-d8 film and a PS-d8 film where the SDS was washed away. There is less contrast between the surface and bulk in the SDS-treated sample, which could account for the elimination of the Tg confinement effect observed in films containing SDS [Chen and Torkelson, Polymer, 2016, 87, 226].


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...