Stretch-induced complexation reaction between poly(vinyl alcohol) and iodine: an in situ synchrotron radiation small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering study
Abstract
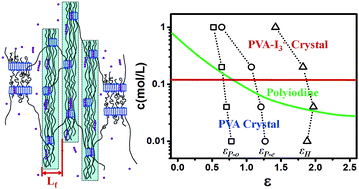
Fibrillation and the complexation reaction between poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA)–iodine (I) complexes have been studied with in situ synchrotron radiation small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS and WAXS) during the uniaxial stretching of PVA films in KI/I2 aqueous solution. SAXS results show that stretching induces the formation of nanofibrils, which pack periodically in the later stage of stretching with an average inter-fibrillar distance of around 10 nm. The onset strains for fibrillation and the appearance of periodicity of nanofibrils are located at the beginning and the end of the stress plateau, and decrease with increasing iodine concentration. In the stretching process as a whole, the presence of iodine ions reduces the crystallinity of the PVA crystal but favors the formation of a PVA–I complex. The complexation reaction is promoted by the synergistic effect of stretch and iodine ions, during which stretching drives the formation of polyiodine via the effect of entropic reduction while iodine concentration dictates crystallization of PVA–I3− co-crystals through the role of chemical potential. A morphological and structural phase diagram is constructed in the strain–iodine concentration space, which defines the regions for fibrillation and complexation reactions and may serve as a roadmap for the industrial processing of PVA polarizer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...