Synthesis of high-density and low-freezing-point jet fuel using lignocellulose-derived isophorone and furanic aldehydes†
Abstract
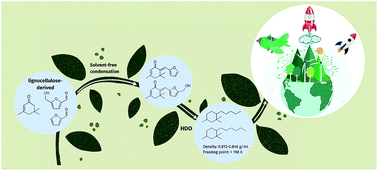
Biofuels synthesized from lignocellulose-derived platform chemicals are very attractive for sustainable development. Here we reported a new and facile route to synthesize multi-substituted cycloalkanes with a high density and low freezing point using isophorone and furanic aldehydes (furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural), by solvent-free aldol condensation, followed by hydrodeoxygenation. Catalysts were screened and NaOH showed good performance. The reaction conditions including catalyst dosage, isophorone/furanic aldehyde ratio, temperature and solvent were optimized, and finally the yields of 70.0% for isophorone/furfural and 72.8% for isophorone/5-hydroxymethylfurfural were obtained. Pt/HZSM-5 was prepared as the bifunctional catalyst for hydrodeoxygenation of the condensed product. The resultant multi-substituted cyclohexanes derived from isophorone/furfural and isophorone/5-hydroxymethylfurfural have a density of 0.813 g mL−1 and 0.846 g mL−1 respectively and both have a freezing point lower than −75 °C, and are very promising as stand-alone fuels or additives of other biofuels.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...