Hollow carbon microtubes from kapok fiber: structural evolution and energy storage performance†
Abstract
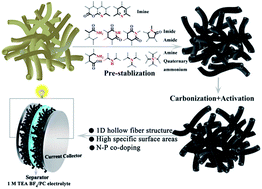
Hollow carbon microtubes, with tunable porosity and surface chemistry, are highly desired for advanced energy conversion and storage applications. Although most natural fibers possess a hollow tubular structure, their original morphology is easily destroyed when they are carbonized directly due to the pyrolysis reactions. In this study, using kapok fiber as a precursor, hollow carbon microtubes were obtained by pre-stabilization and subsequent carbonization–activation in the presence of (NH4)2HPO4. During structural evolution from an organic biomass fiber to a hollow carbon fiber, (NH4)2HPO4 acts not only as a porogen and nitrogen/phosphorus source for in situ activation and doping but also as a crosslinking agent for chemical stabilization. The material exhibited good electrochemical performance in an organic electrolyte when evaluated as a supercapacitor electrode due to highly accessible surface area, convenient ion diffusion, and electron transfer. This study provides insights for the design of an anisotropic porous carbon structure towards next-generation high-power smart devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...