Cyclopentadithiophene derivatives: a step towards an understanding of thiophene copolymer excited state deactivation pathways†
Abstract
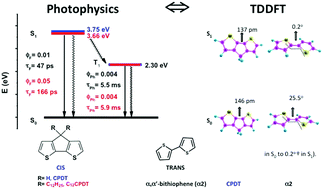
We have carried out the excited state characterization of cyclopentadithiophene (CPDT) and its didodecyl-substituted derivative (C12CPDT) to obtain detailed insights into their photophysical pathways. These are the cis analogues of α,α′-bithiophene (α2), which normally exists in the more stable s-trans geometry. We report absorption, fluorescence, phosphorescence, and triplet-singlet difference spectra, together with quantum yields (fluorescence, phosphorescence and singlet oxygen). Fast time-resolved fluorescence and transient absorption techniques (ps-TCSPC and fs-TA) were used to characterize the initial excited state dynamics of the CPDTs and α2. In general, the two CPDTs show similar spectral and photophysical properties to α2, although phosphorescence is absent in α2 (the trans conformer). From TDDFT calculations it is shown that the large Stokes shift (SS) observed for CPDT and C12CPDT (planar in S0 and S1) is due to a bond length change in the C–C bond connecting the two thiophene units, which decreases from 146 to 137 pm. With α2 this change is accompanied by a change in the dihedral angle (25.5° in S0 to 0.2° in S1).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...