Molecularly imprinted artificial esterases with highly specific active sites and precisely installed catalytic groups†
Abstract
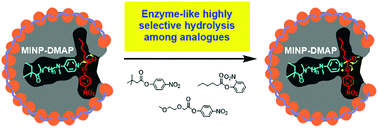
A difficult challenge in synthetic enzymes is the creation of substrate-selective active sites with accurately positioned catalytic groups. Covalent molecular imprinting in cross-linked micelles afforded such active sites in protein-sized, water-soluble nanoparticle catalysts. Our method allowed a systematic tuning of the distance of the catalytic group to the bound substrate. The catalysts displayed enzyme-like kinetics and easily distinguished substrates with subtle structural differences.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
