Heteroaryl-linked norbornadiene dimers with redshifted absorptions†
Abstract
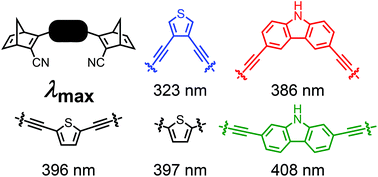
Development of Molecular Solar Thermal (MOST) systems for harvesting and storing solar energy is based on molecular photoswitches that undergo photoisomerizations to metastable isomers. One challenge is to achieve low-molecular weight molecules that absorb at sufficiently long wavelengths to match the solar spectrum. Here we show that this can be achieved by linking two norbornadiene (NBD) photoswitches to a central heterocycle, thiophene or carbazole, via alkyne appendages. In this approach, the same heteroaryl is used to tune the properties of two photoswitches at the same time, thereby keeping the molecular weight as low as possible. A series of NBD dimers was prepared by Sonogashira coupling reactions, and these compounds showed remarkable redshifted absorptions, with onsets of absorption as high as 468 nm, and thermal half-lives ranging from 44 seconds to 16 hours.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Mechanistic, computational & physical organic chemistry in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...