Consecutive Lossen rearrangement/transamidation reaction of hydroxamic acids under catalyst- and additive-free conditions†
Abstract
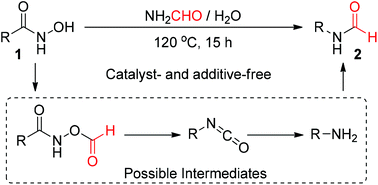
The Lossen rearrangement is a classic process for transforming activated hydroxamic acids into isocyanate under basic or thermal conditions. In the current report we disclosed a consecutive Lossen rearrangement/transamidation reaction in which unactivated hydroxamic acids were converted into N-substituted formamides in a one-pot manner under catalyst- and additive-free conditions. One feature of this novel transformation is that the formamide plays triple roles in the reaction by acting as a readily available solvent, a promoter for additive-free Lossen rearrangement, and a source of the formyl group in the final products. Acyl groups other than formyl could also be introduced into the product when changing the solvent to other low molecular weight aliphatic amide derivatives. The solvent-promoted Lossen rearrangement was better understood by DFT calculations, and the intermediacy of isocyanate and amine was supported well by experiments, in which the desired products were obtained in excellent yields under similar conditions. Not only monosubstituted formamides were synthesized from hydroxamic acids, but also N,N-disubstituted formamides were obtained when secondary amines were used as precursors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...