Ribosomal incorporation of backbone modified amino acids via an editing-deficient aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase†
Abstract
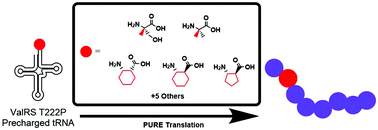
The ability to incorporate non-canonical amino acids (ncAA) using translation offers researchers the ability to extend the functionality of proteins and peptides for many applications including synthetic biology, biophysical and structural studies, and discovery of novel ligands. Here we describe the high promiscuity of an editing-deficient valine-tRNA synthetase (ValRS T222P). Using this enzyme, we demonstrate ribosomal translation of 11 ncAAs including those with novel side chains, α,α-disubstitutions, and cyclic β-amino acids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...