Silica coating enhances the stability of inorganic perovskite nanocrystals for efficient and stable down-conversion in white light-emitting devices†
Abstract
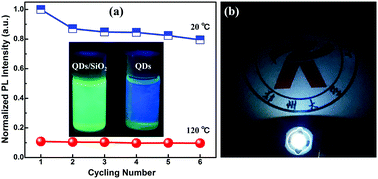
Recently, inorganic halide perovskite (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, I) quantum dots (QDs) have attracted tremendous research interests because of their great potential for application in the fields of low-cost light sources and displays. However, the unsatisfactory structural and chemical stabilities of such materials are the main obstacles hindering reliable device operation significantly. In this study, we successfully prepared CsPbBr3/silica QD composites through a simple sol–gel reaction by using tetramethoxysilane as a single molecule precursor. The as-prepared CsPbBr3/silica QD composites demonstrated substantially improved stability against heat, light, and environmental oxygen/moisture. Besides, a relatively narrower photoluminescence linewidth and higher quantum yield were achieved compared with that of fresh CsPbBr3 QDs. Furthermore, the CsPbBr3 QDs/silica composites were applied as color-converting layer curing on blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for white LED applications. Finally, a high power efficiency of 63.5 lm W−1 was obtained and the light emission could be efficiently sustained over 13 h without any decay in the continuous current mode, demonstrating remarkable operation stability than that reported previously. It can be anticipated that the excellent properties and facile processing technique used here will make perovskite QDs/silica composites attractive for applications in optoelectronics and industrial fields.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...