The influence of surface functionalization methods on the performance of silicon nanocrystal LEDs†
Abstract
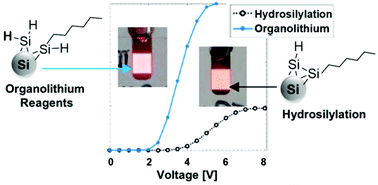
The influence of silicon nanocrystal (SiNC) surface characteristics obtained from different functionalization methods on the performance of LEDs was investigated. The surface of SiNCs was functionalized with hexyl chains via hydrosilylation (HS) or with organolithium reagents (OLR) and resulting SiNCs were incorporated as the emissive layer in hybrid organic/inorganic LEDs. Devices utilizing SiNCs functionalized with OLR consistently exhibited lower turn-on voltages, higher luminances and external quantum efficiencies compared to those obtained from the HS method. These improvements were attributed to the less dense and monolayer surface coverage of the SiNCs obtained by the OLR method, as well as their higher absolute quantum yield.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...