A photonic sintering derived Ag flake/nanoparticle-based highly sensitive stretchable strain sensor for human motion monitoring†
Abstract
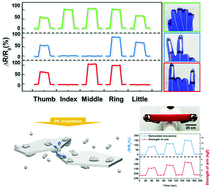
Recently, the demand for stretchable strain sensors used for detecting human motion is rapidly increasing. This paper proposes high-performance strain sensors based on Ag flake/Ag nanocrystal (NC) hybrid materials incorporated into a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer. The addition of Ag NCs into an Ag flake network enhances the electrical conductivity and sensitivity of the strain sensors. The intense localized heating of Ag flakes/NCs is induced by intense pulsed light (IPL) irradiation, to achieve efficient sintering of the Ag NCs within a second, without damaging the PDMS matrix. This leads to significant improvement in the sensor sensitivity. Our strain sensors are highly stretchable (maximum strain = 80%) and sensitive (gauge factor = 7.1) with high mechanical stability over 10 000 stretching cycles under 50% strain. For practical demonstration, the fabrication of a smart glove for detecting the motions of fingers and a sports band for measuring the applied arm strength is also presented. This study provides an effective method for fabricating elastomer-based high-performance stretchable electronics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...